WANTED: Individual or team to take over this project. I'm in my 70's and want to put my feet up. Contact details in footer.
Glossary |
|
Item Level |
Summary Text |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
0 GCSE |
Logic zero is any voltage below half the power supply voltage, often close to zero Volts. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
1 GCSE |
Logic one is any voltage above half the power supply voltage, often close to the power supply voltage. |
|
1G GCSE |
The oldest mobile phone technology from 1979. Analogue signals only. Phones were the size and weight of a house brick. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
2N AS Level |
How many values can a five bit number represent? 25 = 32. There are many more problems similar to this one. How many colours can be represented by an eight bit pixel? 28 = 256. How many addresses can a ten bit address bus access? |
|
2G GCSE |
Second generation mobile phone technology. This uses encrypted digital radio transmissions between the cell mast and the phone. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
386 GCSE |
This is a useful audio amplifier chip giving at least 0.25 Watts output. The data sheet lists the powers available from the various chip versions. |
|
3G GCSE |
Third generation mobile phone technology. This was faster and made Internet connections possible. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
40106 GCSE |
The 40106 chip contains six Schmitt Trigger NOT gates. The NOT gate inverts its input signal. A normal NOT gate changes state when the input signal crosses half of the power supply voltage. With Schmitt gate inputs, the level has to rise above 2/3 and drop below 1/3 of the power supply. |
|
4013 GCSE |
D Type Flip Flop chip.
|
|
4017 GCSE |
A decade counter chip with ten outputs numbered from 0 to 9.
|
|
4G GCSE |
Fourth generation mobile phone technology. This was fast enough to stream high definition video to a phone. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
555 GCSE |
The timer chip used to make Monostable and Astable circuits.
|
|
5G GCSE |
Fifth generation mobile phone technology. This is able to use active antennas that beam their energy in the correct direction for each connected phone. This allows far more phones to connect to one cell and even higher speeds are possible. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
741 GCSE |
A cheap, low performance but well behaved operational amplifier chip. It has a very high open loop gain and input resistance close to infinity. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
A to D Converter GCSE |
This converts smoothly varying signals that occur in nature into the two digital levels used by computers and other digital signal processing systems like phones and personal stereos. The analogue levels are often represented by binary numbers. |
|
Absolute Position A Level |
The position is fully known. See Relative Position. |
|
Absolute Zero GCSE |
Warm atoms and electrons vibrate randomly. Hot ones vibrate more. Realy hot stuff vibrates enough to radiate light (red or white hot). At about -273C or absolute zero, all atomic and electron vibration ceases. In electronics this is useful. Very low noise amplifiers can be built. At these low temperatures, some materials become superconductors. Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature in Physics. |
|
AC GCSE |
See Alternating Current. |
|
Accuracy GCSE |
Resistors are manufactured with precisions of +/- 1, 2, 5 or 10%. Capacitors are commonly accurate to +/- 5%. When calculating, electronic engineers mostly quote answers to two or three significant figures. More digits are pointless because the circuit can't be built to that level of precision. An exception is with the design and manufacture of precision measuring instruments. |
|
Active GCSE |
Components, usually semiconductors, with high frequency voltage, current or power gain. |
|
Active Filter A Level |
A filter built with resistor/s, capacitor/s and an Op Amp. See Filters. |
|
Active High GCSE |
A high input voltage or logic ONE is needed to turn on a circuit or device. Example: Transistor Switch. |
|
Active Low GCSE |
A low input voltage or logic ZERO is needed to turn on a circuit or device. Example: Bistable Latch. |
|
Actuator GCSE |
An output transducer that provides mechanical movement. Examples include solenoids, motors and servos. |
|
ADC GCSE |
See Analogue to Digital Converter. |
|
ADC Half Flash A Level |
Instead of using a single six bit flash ADC needing 63 comparators (2N - 1), you can use two three bit flash ADCs each needing 7 comparators. Some additional components are needed but this solution is much simpler and only slightly slower in operation. Two eight bit half flash converters can emulate a sixteen bit converter. In this case the component saving is even greater. |
|
addlw k A Level |
MPASM: (W) + k → W The contents of the W register are added to the eight bit literal 'k' and the result is placed in the W register. |
|
Address A Level |
Addresses uniquely identify one and only one memory location or I/O Port. This guarantees that only one tristate device ever has access to the data bus at any time. |
|
Aerial GCSE |
See Antenna. |
|
AF GCSE |
Audio Frequency. 20 to 20000 Hz or 300 to 3000 Hz for telephone quality. |
|
AF Amplifier GCSE |
A.F. is the range of frequencies people can hear. It runs from 20 Hz to 20000 Hz. For telephone quality voice, the range of frequencies is from 300 Hz to 3000 Hz. An audio amplifier increases the magnitude of audio signals. |
|
AGC A Level |
See Automatic Gain Control. |
|
Aliasing A Level |
Unwanted patterns in still images. Unwanted frequencies in audio. Strange visual effects in motion video. The sampling frequency must be at least double the highest information signal frequency. If this is not the case, aliasing occurs. |
|
Alternating Current GCSE |
Cells and batteries produce a steady flow of electrons called Direct Current. Alternating current flows backwards and forwards 50 times per second (Europe) or 60 times (USA). Alternating current is useful because the voltage can be stepped up or down using a transformer. This makes high voltage power distribution possible. High voltage, low current power distribution is more efficient and transformers are needed to make this work. Mains power is AC. |
|
AM GCSE |
See Amplitude Modulation. |
|
Ammeter GCSE |
This measures current. Break the circuit. Put the ammeter into the circuit break so the current now flows through it. An ideal ammeter has no resistance. The voltage across an ideal ammeter is zero. |
|
Amp (Ampere) GCSE |
Current is measured in Amps. One amp is 6.24 x 1018 electrons passing a point each second. |
|
Amplifier GCSE |
This increases the magnitude of the input signal.
|
|
Amplitude GCSE |
A measurement of the height of a wave from the centre line. |
|
Amplitude Modulation GCSE |
The carrier amplitude is modified proportional to the information signal amplitude. AM is used in the LF, MF and HF broadcast bands. The AM bandwidth is double the highest frequency in the information signal. |
|
Analogue Signals GCSE |
Smoothly varying signals that occur in nature. The signals have an infinite range of values between a minimum and a maximum unlike digital signals where there are only two levels. |
|
AND GCSE |
AND Gate. The output is ONE if all the inputs are ONE. ZERO otherwise. |
|
andlw k A Level |
MPASM: (W) .AND. (k) → W The contents of W register are AND’ed with the eight bit literal 'k'. The result is placed in the W register. |
|
Angular resolution A Level |
The smallest angular rotation that can be made or detected. For example: A 360o disc is divided into four tracks giving a 16 value Gray code. The angular resolution is 360 / 16 = 22.5o. |
|
ANN A Level |
See Artificial Neural Network. |
|
Antenna A Level |
A receiving antenna is a transducer that converts electromagnetic radiation (radio waves) into an alternating voltage or current. A transmitting antenna does the same conversion in reverse. The most common antenna is a wire or rod, half a wavelength long, called a half wave dipole. |
|
Architecture A Level |
This describes the design and layout of the inner workings, usually of microcontrollers or microprocessors. |
|
Armature A Level |
Usually the moving part of a motor. It's complex. Check out Wikipedia. |
|
Artificial Neural Network Extras Non Exam |
|
|
Assembler A Level |
The Assembler program translates human-readable assembly code into binary numbers or machine code understood by the microcontroller. It automatically calculates the addresses of labels, jumps and subroutines saving the programmer a lot of time and preventing unnecessary mistakes. |
|
Astable GCSE |
An oscillator with zero stable states. It produces a square wave alternating output. The 555 chip is commonly used but op amp and logic gate astables are possible too. |
|
Asynchronous A Level |
Signalling where the sender and receiver have separate clocks and it's impossible to predict when a signal will start arriving. Pulses arrive at unpredictable time intervals. See synchronous. |
|
Atom GCSE |
Matter is made of atoms. The atom is the smallest indivisible piece of an element.
|
|
Attenuation AS Level |
This is the signal becoming weaker as it travels further from the transmitter. Sometimes a very large signal needs to be attenuated before it can be processed. |
|
Automatic Gain Control A Level |
This uses negative feedback to control the gain of a radio receiver to maintain a constant audio output at the loudspeaker, even if the received signal strength varies. |
|
Autonomous A Level |
Robots with artificial intelligence that enables them to function without continuous human intervention. For example, the Mars rovers are autonomous because interactive control is impossible due to the time it takes radio signals to reach Mars and return to Earth. |
|
AVR A Level |
A family of microcontroller PICs made by Atmel. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Back EMF GCSE |
When the current in an inductor (coil) changes, a back EMF voltage spike is produced. Sudden current changes cause large and possibly damaging back EMF spikes. To prevent damage, the current must be allowed to change more slowly. Correctly positioned diodes allow the current to die away slowly solving the problem. |
|
Bandwidth GCSE |
A measure of the capacity of a channel to carry information.
|
|
Bandwidth (Amplifiers) GCSE |
The range of frequencies over which ...
|
|
Base Station A Level |
Mobile phones connect by radio to the nearest Base Station or Cell. |
|
Baseband GCSE |
This is the low frequency information signal such as Audio or Keyed or Switched DC. Baseband signals are often multiplexed using time division multiplexing. See Broadband. |
|
Bass GCSE |
Low audio frequencies from 20 Hz to 300 Hz. BIG loudspeaker drivers are needed to reproduce good bass. See Treble and Mid-Range. |
|
Battery GCSE |
Chemical storage of electrical energy. Batteries provide an EMF (electron moving force or voltage). A battery contains two or more cells. |
|
Baud Rate A Level |
The number of bits per second sent or received in a communications system. Baud rate includes all the bits, some of which are data and some used to manage the data flow. In broadband communications, advanced techniques make it possible to send several bits in one baud. See QAM. |
|
BCD GCSE |
BCD means Binary coded decimal. 129 decimal converts to 10000001 in normal binary. In BCD, each decimal digit is converted to a four bit binary number so 129 becomes 0001 0010 1001. BCD is useful for calculators, clocks, weighing scales and and any display where decimal digits have to be displayed. |
|
bcf f, b A Level |
MPASM: 0 → f Bit 'b' in register 'f' is cleared (set to zero). |
|
Bias GCSE |
|
|
Binary GCSE |
|
|
BIOS GCSE |
Basic Input Output System - This is firmware stored in ROM or non-volatile Flash Memory. Typically it provides keyboard and screen facilities to allow a new computer to be configured for the first time. It also initiates the boot sequence allowing the chosen operating system/s to load. Microcontrollers contain a minimal BIOS to allow the chip to be programmed. |
|
Bistable Latch GCSE |
Made from two NAND gates - also known as an RS Flip FLop
|
|
Bit GCSE |
A binary digit. A Zero or a One.
|
|
Bit Mask GCSE |
A binary pattern used to keep or discard bits usually using the AND operation. If the mask bits are 1, the data is kept. If the mask bits are 0, the data is cleared. OR masking is possible and the ignored bits are forced to ONE. XOR masking inverts the bits of interest. This is widely used in animated computer graphics to make shapes appear or disappear. |
|
Bit Rate GCSE |
The number of bits per second sent or received in a communications system. Baud rate includes all the bits, some of which are data and some used to manage the data flow. Bit rate counts the data bits per second excluding the management bits. |
|
BJT GCSE |
Bipolar Junction Transistor. A small base current controls a much larger emitter / collector current. The current gain is calculated from Ic / Ib. |
|
Boolean GCSE |
Boole invented Boolean Algebra for processing TRUE and FALSE values used in Logic Gates. Boolean values are usually written down with 0 and 1 symbols. |
|
Boot GCSE |
The bootstrap program is stored in ROM and it starts up the computer. It looks for an operating system in the boot sector of the boot disk. It it finds this, it launches the program and your chosen operating system starts up. In a microcontroller, the bootstrap might be as simple as "GOTO 0x0000" |
|
Break Frequency AS Level |
At the break or breakpoint frequency of a filter the output voltage drops to 0.7 of the maximum output voltage. The reactance of the capacitor is equal to the resistance of the resistor. See also: cut off frequency. |
|
Breakdown GCSE |
Breakdown voltage is the largest voltage a component can stand before it breaks down. When a component breaks down, it is usually destroyed by the large current that flows. A few components such as Zener Diodes are designed to be used in the broken down state and it's important to limit the current to a safe level with a suitable resistor. |
|
Bridge Rectifier GCSE |
Four diodes used to convert AC into DC. Sometimes all four diodes are wired into one plastic moulding with four pins. |
|
Broadband GCSE |
More than one (often hundreds) of high frequency carriers are modulated with the the low frequency information signal such as Audio or Keyed or Switched DC. Broadband signals are multiplexed using frequency division multiplexing. See Baseband. |
|
Broadcast GCSE |
A one way transmission transmitted to many recipients. Radio and TV are well known examples. The transmission channel can not be used to send a reply reply to the sender. This is also called simplex. In computer networks, hubs broadcast received frames (or packets) out to all the devices plugged into the hub. In computer networks, switches learn the addresses of the connected devices and selectively send received frames (or packets) out to the correct the device. |
|
BS 1852 GCSE |
A British Standard notation for labelling components. 4K7 means 4.7 kΩ |
|
bsf f, b A Level |
MPASM: 1 → f<b> Bit 'b' in register 'f' is set (set to one). |
|
btfsc f, b A Level |
MPASM: skip if (f<b>) = 0
If bit 'b' in register 'f' is '0' then the next instruction is skipped. |
|
btfss f, b A Level |
MPASM: skip if (f<b>) = 1
If bit 'b' in register 'f' is '1' then the next instruction is skipped. |
|
Buffer GCSE |
Buffer circuits isolate the input device from the buffer output by having a very high input impedance. Buffers can often provide quite large output currents. These are called drivers. Tristate buffers can disconnect their output from a shared bus, allowing other devices to share the same bus. |
|
Bulb GCSE |
An output transducer that converts electric current into heat and light by heating a tungsten filament white hot. These are being replaced by more efficient and longer lasting LED and gas discharge lamps. |
|
Bus A Level |
A collection of wires shared between multiple devices. This arrangement simplifies the interconnection of the devices.
|
|
Bus Contention A Level |
Only one device can write to the bus at any time. If more than one device needs to write to the bus this must be safely managed. |
|
Buzzer GCSE |
This transducer produces a buzzing sound and it needs a DC power source. It generates its own alternating signal to make the buzz. See Sounder. |
|
Byte GCSE |
A group of eight bits.
|
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
call k A Level |
MPASM: (PC) + 1 → TOS k → PC<10:0> (PCLATH<4:3>) → PC<12:11>
Call Subroutine. |
|
Capacitor A Level |
Two metal plates separated by an insulator. The plates can be made from thin foil and rolled up into the common tubular capacitor shape. Capacitors store energy in the form of electronic charge. The biggest high voltage capacitors can store enough energy to deliver a fatal electric shock. XC = 1 / ( 2 π f C ) Capacitance C is defined as Q / V or the number of charge Coulombs stored per Volt.
|
|
Carrier A Level |
This is a high frequency signal, usually for radio transmission. The carrier is modulated (modified) to include the information signal to be transmitted. It's needed because the frequency of the information signal is usually far too low to be transmitted by radio without the help of the carrier. Broadband uses many (even hundreds of) carriers. Each carries digital data at a low rate. Combined, the data throughput is large. |
|
Cell A Level |
Mobile phone networks rely on overlapping cells covering the entire country. If a phone moves from one cell to another, the call is automatically transferred to the new cell. Each cell has its own transmitters, receivers and antenna mast. |
|
Cell GCSE |
Chemical storage of electrical energy. Two or more cells make a battery. |
|
Centi GCSE |
S.I. Units Prefix: 1 / 100 10-2 |
|
Characteristic Curve GCSE |
These are graphs, usually showing voltage and current. They describe the performance of a component. Sometimes voltage / frequency or other types of graph are useful. |
|
Charge GCSE |
Charge is measured in coulombs.
|
|
Chip GCSE |
An self contained integrated circuit containing transistors, resistors and capacitors. The chip solves an electronic problem like timing, amplifying, logic or arithmetic. |
|
Circuit GCSE |
A collection of electronic components performing a useful task. Current will not flow until the circuit is complete (without gaps). |
|
Circuit Diagram GCSE |
A diagram showing the electronic component symbols and how they are connected. These diagrams are often confused with system diagrams, layout diagrams and flow charts. |
|
Circuit Switched Network A Level |
The original telephone network was circuit switched. It's being replaced by the more efficient and cheaper Packet Switched networks. |
|
Class A/B/C/D Amplifiers A Level |
|
|
Clear GCSE |
The output goes low, becomes zero. See Set. |
|
Clipping GCSE |
The amplifier is trying to generate an output greater than the power supply voltage so the top/bottom of the signal is flattened or clipped. This happens at high volumes. It's also called limiting or saturation. |
|
Clock GCSE |
A square wave signal used to synchronise all operations in a logic, computer or communications system. |
|
Closed Loop AS Level |
A control system with negative feedback. The output is measured and fed back to the input in order to correct errors in the output. See Open Loop. |
|
clrf f A Level |
MPASM: 0 → f The contents of register 'f' are cleared and the Z bit is set. |
|
Co-axial Cable A Level |
This is a screened cable with a centre conductor and a woven braid screening layer. The screening layer keeps the wanted signal inside the cable and prevents outside noise or cross-talk signals getting in. |
|
Codec A Level |
Digital encoder and decoder to modulate and demodulate digital transmissions. |
|
Coil GCSE |
Wire wound into a spring shape. Coils act as electromagnets and are useful in filters and tuned circuits. Larger coils with an iron core are used in Solenoids, Electromagnetic Relays and Transformers. |
|
Combinational Logic GCSE |
Logic gates without a memory or a clock. The output changes as soon as the input changes. |
|
comf f, d A Level |
MPASM: (f) → d The contents of register 'f' are 1's complemented. If 'd' is 0 the result is stored in W. If 'd' is 1 the result is stored back in register 'f'. |
|
Common GCSE |
In a switch this connection is always connected to the circuit. The NO and NC connections are made by operating the switch. |
|
Common Anode GCSE |
In LED bars and arrays and Seven Segment displays, all the LED anodes are connected together and wired to a single pin. |
|
Common Cathode GCSE |
In LED bars and arrays and Seven Segment displays, all the LED cathodes are connected together and wired to a single pin. |
|
Communication GCSE |
The transfer of meaningful information from the sender to the receiver. |
|
Comparator GCSE |
Operational amplifiers have a very high open loop gain. The comparator op-amp compares its two input voltages. The output is always either low or high because the op-amp voltage gain is so high. If the non inverting input is greater than the inverting input, the output will be high and vice versa. The comparator is a one bit A to D converter. |
|
Complete Instruction Set A Level |
The CISC chip has a large number of complex instructions built into it. It uses hardware to do most computations. The simpler RISC chips rely on software to solve similar problems. RISC chips are simpler and use much less power. |
|
Components GCSE |
Resistors, Capacitors, Transistors, MOSFETs and all the other devices that can't be broken up into smaller sub-systems. |
|
Conductor GCSE |
A material in which the outer electrons are free to wander away from their parent atoms. If a potential difference is applied to this material, there will be a net flow of electrons and a current will flow. |
|
Control System GCSE |
Input sensor/s processes and output devices, sometimes with negative feedback. |
|
Coulomb GCSE |
The measurement unit of electronic charge. One coulomb = 6.25x1018 electrons. |
|
Coupling A Level |
Getting a signal from one subsystem into another. Coupling capacitors are commonly used. |
|
Cross-Over Distortion GCSE |
The input signal is too small to turn on either MOSFET (or Bipolar Junction Transistor). The output disappears when the input voltage crosses over the zero line. This sounds harsh and unpleasant. It is cured by biasing the MOSFETs (or transistors) with diodes and resistors and also by including the MOSFETs (or transistors) in the negative feedback path. |
|
Crosstalk A Level |
Crosstalk is unwanted leakage of a signal from one channel to another. It can be caused by capacitative or magnetic coupling of the signal. More rarely it could be caused by leakage through poor insulation. It is greatly reduced by the twists in twisted pair cables and the screening layer in co-axial cable. |
|
CTCSS A Level |
Continuous Tone Coded Squelch System. A tone below 300 Hz. The receiver will not operate unless the correct tone is present. The tone is filtered out before audio is sent to the speaker. This allows multiple organisations to share the same radio channels without having to listen to each other's transmissions. Each uses a different tone. |
|
Current GCSE |
This is a net flow of charged particles (usually free electrons). The flow is measured in Amps or Amperes. Electrons flow away from negative voltages towards the positive. For current to flow, there must be a potential difference and a complete circuit. In liquids, charged ions flow. In a plasma, charged atoms, molecules and free electrons flow. |
|
Cut off frequency A Level |
See break or breakpoint frequency. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
D to A Converter GCSE |
Computers only store digital data as ONEs and ZEROs. For a computer to play back audio or video, the digital data has to be converted back into analogue. |
|
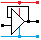
D Type Flip Flop GCSE |
On the rising edge of the clock pulse, the input D is copied to the output Q.
|
|
DAB A Level |
Digital Audio Broadcasting using 1536 carriers for each multiplex with each carrier digitally modulated at 1.5 kb/s (a low data rate). |
|
DAC GCSE |
See Digital to Analogue Converter. |
|
Damping A Level |
How quickly a machine or signal reaches its final setting.
|
|
Darlington Driver GCSE |
A bipolar transistor switch using two transistors instead of one. It has an extremely high current gain. |
|
Data GCSE |
Meaningful information.
|
|
DC GCSE |
See Direct Current. |
|
De Morgan GCSE |
These can be used to simplify logic circuits or expressions. A + B = A . B A . B = A + B |
|
Debouncing GCSE |
Switch bounce is a problem if the switch operations are being counted. The problem is caused by mechanical bouncing of the switch contacts. It is cured with a debouncing circuit. |
|
decfsz f, d A Level |
MPASM: (f) - 1 → d skip if result = 0
The contents of register 'f' are decremented. |
|
Decibel A Level |
Decibels dB are a measurement scale where the numbering multiplies instead of adding. 1, 10, 100, 1000. This allows the scale to cover a vast range of values. Decibels compare a signal with a reference level or compare the signal level with the noise level. |
|
Decimal GCSE |
The 10 symbol number system used in every day life. |
|
Decision GCSE |
For example:
|
|
Decoder GCSE |
Binary numbers can be decoded.
|
|
Decoupling GCSE |
Getting rid of unwanted AC signals by coupling them to ground through a capacitor. |
|
Decrypting A Level |
Decode an encoded or encrypted signal.
|
|
Demodulator GCSE |
A circuit the separates the information signal from the modulated carrier signal. The output might be music, speech or control signals as in radio control. Also known as a detector or decoder. |
|
Detector GCSE |
This is another name for a demodulator. |
|
Digital GCSE |
Signals with only two levels ZERO/ONE or LOW/HIGH. Digital signals perform well because unwanted noise can usually be removed resulting in error free signals. |
|
Digital Ramp ADC AS Level |
A slow, cheap analogue to digital converter, It's OK for audio and human manual interaction with joysticks or push buttons. |
|
Digitise GCSE |
Convert an analogue signal into digital. |
|
Diode GCSE |
Passes current in one direction only.
|
|
Dipole A Level |
The dipole antenna is half a wavelength long. It is usually connected to a transmitter or receiver with 50 Ω co-axial cable. If the dipole length is wrong, it will be less efficient and there will be an impedance mismatch - no longer 50 Ω. |
|
Dipole Half-wave A Level |
The dipole antenna is half a wavelength long. C = F λ |
|
Direct Current GCSE |
This is a steady unvarying voltage or current. Batteries and low voltage power supplies produce DC. See Alternating Current. |
|
Dispersion A Level |
|
|
Distortion AS Level |
Amplifiers should be linear. The output should be exactly proportional to the input. In real life this is hard to achieve so the output is distorted. Two common types of distortion are cross-over distortion with small signal inputs and clipping or limiting with large signal inputs. Don't confuse distortion with noise. |
|
Dope AS Level |
Tiny amounts of impurities added to intrinsic (pure) semiconductors. The impurities control the electronic properties of the semiconductors. Boron and Phosphorus are commonly used dope materials diffused into the intrinsic Silicon. |
|
Downlink A Level |
A radio signal from a satellite down to the Earth such as satellite TV reception. Also a signal from the cell base station to a mobile phone. See Uplink. |
|
Driver GCSE |
This is a switch or follower circuit with a tiny current input and a much larger current output. They drive relays, motors, lamps and many other higher power devices. The circuit is needed because the microcontroller, comparator or other process circuit can not drive the load on its own. |
|
Duplex A Level |
The capabilities of a communications channel.
|
|
Dynamic Range AS Level |
Systems that can handle a wide range of signal levels without noise or distortion have a good dynamic range. Digital systems often have extremely good performance. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
E24 GCSE |
These resistors are available in catalogues for purchase. There are 24 values per decade. For example between 1kOhm and 9.1kOhm, there are 24 values available. |
|
Earth / Ground GCSE |
This is a zero volt reference level. It's important for electrical safety. By definition the whole planet is at zero volts although locally this might not be true. The earth wire in a mains plug is very close to the zero volts earth potential unless there is a fault. |
|
Electromagnetic Waves GCSE |
These are radio waves. They travel in straight lines through air or a vacuum at the speed of light, 300 million metres per second. Shorter wavelengths at higher frequencies include microwaves, infra-red, visible light, ultra-violet, x-rays, gamma-rays and cosmic-rays. |
|
Electrons GCSE |
Electrons are tiny negatively charged subatomic particles. Each atom is surrounded by a cloud of electrons. Normally the negative charge of the electrons is exactly balanced by the positive charge of the atomic nucleus. Electronic circuits rely on the behaviour of electrons in different materials. |
|
EMF GCSE |
This is electromotive force or electron moving force measured in Volts. The term EMF is applied to cells, batteries, dynamos, alternators, photovoltaic cells and any other power sources that create their own volts. |
|
Encapsulation GCSE |
One example is the wrapping data into IP packets, adding origin and destination addresses, the packet type and an error checksum. |
|
Encoding GCSE |
The process of producing a digitally modulated signal. There are many types of encoding for text, music and video. |
|
Encrypting GCSE |
Encode a signal so it can not be read unless you also possess the key to decrypt. |
|
Energy GCSE |
Energy is measured in Joules. It can not be created or destroyed. It can be converted from one type to another. In Electronics, transducers convert energy between electrical and other forms. Energy must be transferred to "do work" such as producing light, sound, acceleration, lifting against the force of gravity or heating something up. |
|
Ethernet GCSE |
The most widely used local area network (LAN) protocol with fairly simple rules.
|
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Fading A Level |
Variations in the signal strength of received radio signals. This often happens if the signals arrive by more than one path due to reflections off terrain, buildings, vehicles or the ionosphere. If the signals arrive out of phase, they cancel out. If they arrive in phase, the signals add and appear stronger. |
|
Farad GCSE |
The measurement unit of capacitance. |
|
Feedback AS Level |
The output is measured and fed back to the input.
|
|
Feeder A Level |
The co-axial cable, open wire feeder or wave-guide used to connect an antenna to a transmitter or receiver. |
|
Ferrite A Level |
A non-conducting magnetic material. One type of ferrite is made with iron dust and non-conducting resin. Ferrite is useful in RF Tuned Circuits and Filters. Adding ferrite to a coil greatly increases its inductance. |
|
Fibre Optics GCSE |
See optical fibre. |
|
Filter A Level |
Circuits used to block or pass signals at particular frequencies or over a range of frequencies. See Bandwidth.
|
|
Firmware GCSE |
Software stored in non-volatile read only memory (ROM). The software is essential to the operation of the device. Microcontrollers have firmware, allowing the chips to be programmed. More complex computers have firmware that starts the boot process. |
|
Flash ADC A Level |
A high speed, complex, more expensive ADC useful for converting video and radio frequency signals into a digital format. See Digital Ramp ADC. |
|
Flow Charts GCSE |
These diagrams show the sequence and timing of inputs, processes, decisions and outputs in an electronic process. These diagrams are often confused with system diagrams, circuit diagrams and layout diagrams.
|
|
FM A Level |
Frequency Modulation.
|
|
Follower Circuits AS Level |
|
|
Forward Voltage GCSE |
This applies to diodes, LEDs and the base emitter junction of a transistor. When current is flowing, there is a typical voltage across the device which does not depend greatly on the size of the current.
|
|
Free Space A Level |
Electromagnetic radiation can travel through free space. This is a vacuum. Air comes really close to free space. The opposite of free space is cables and optical fibres. |
|
Frequency GCSE |
This is the number of complete cycles of a wave in one second. It is measured in Hertz. |
|
Frequency Divider GCSE |
The digital output frequency is half the input clock frequency. The output mark space ratio is 1:1. D Type Flip Flops are commonly used for this. |
|
Frequency Modulation GCSE |
The carrier frequency is altered or modulated in proportion to the information signal. |
|
Frequency Response GCSE |
The range of frequencies over which a component or circuit is useful. For human audio microphones, speakers and amplifiers, 20 Hz to 20 000 Hz is desirable. For bats, smaller animals and insects, frequencies well above 20 kHz are needed. For elephants, frequencies well below 20 Hz are needed. |
|
Full Wave Rectifier GCSE |
Power supplies with two of four diodes rectify both halves of the AC cycle. |
|
Fuse GCSE |
A very thin wire designed to melt if the current is larger than some safe value. When the wire melts, the circuit is turned off for safety. If the wrong fuse is used and too much current flows there is a serious fire risk. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Gain GCSE |
Voltage Gain = VOUT / VIN Current Gain = IOUT / IIN Power Gain = POUT / PIN |
|
Gain Bandwidth Product AS Level |
This parameter tells you how well an amplifier might perform at higher frequencies. The GBP of an amplifier might be 1000000. At 5000Hz, the maximum possible gain would be 1000000 / 5000 = 200. |
|
Gates GCSE |
These logic gates perform electronic switching according to well defined rules. The gates ...
|
|
Gateway Router GCSE |
The router that connects your own local network to the cloud or internet. |
|
Giga GCSE |
S.I. Units Prefix: 1 000 000 000 109 |
|
Glitch GCSE |
Short unwanted pulses. Power supplies sometimes deliver unwanted pulses caused by lightning strikes or switching from one power source to a different one. Multiplexed displays have glitches while the display is updated because each character or digit is atered, one at a time. Often this is so quick that normal people don't notice. Here is an example. |
|
goto k A Level |
MPASM: k → PC<10:0> PCLATH<4:3> → PC<12:11>
GOTO is an unconditional branch. |
|
Gray Code A Level |
A scale used in robotics for absolute position sensing. It is better than a binary scale because there is never ambiguity because only ever one bit changes at a time with the Gray code. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
H Bridge AS Level |
A motor controller using four MOSFET or Transistor switches. Forwards, reverse and speed control are possible. |
|
Hardware GCSE |
This is the physical stuff that computers are made of. It breaks if you drop it or spill your drink over it. See Software. |
|
Hardwired GCSE |
Permanently soldered circuits with a single function. Compare these with programmable circuits which can be altered by re-programming. |
|
Harvard Architecture AS Level |
A microcontroller architecture with an extra instruction bus. Processing is faster because the instruction can be fetched at the same time as the data. |
|
Heat-Sinks GCSE |
are used to remove waste heat from a circuit.
|
|
Henry GCSE |
The measurement unit of Inductance. |
|
Hertz GCSE |
The unit of measurement of frequency. One Hertz means one complete cycle per second. |
|
Heterodyne Extras Non Exam |
The sum and difference beat frequencies produced when two signals on different frequencies are mixed. Heterodynes can be audible as a whistling tone. In a superhet receiver, they are outside the range of human hearing. |
|
Hexadecimal GCSE |
The base 16 number system. It's used because it makes a neat shorthand for binary nybbles. |
|
HF A Level |
The HF radio band is from 3 to 30MHz. It's also known as Short Wave. |
|
High GCSE |
An output voltage more than half the power supply voltage, often close to the power supply voltage. High may also be called True, One, Set or Yes. See Low. |
|
Host A Level |
Any networked computing device, including computers, printers and devices connected to the "Internet of Things". |
|
Hum GCSE |
Mains circuits work at high voltages and sometimes high currents. Sensitive amplifiers can easily pick up stray, unwanted hum from the mains. This is a low pitched 50 Hz tone (60 Hz USA) often with other noise included because the mains is rarely a clean sine wave. Co-axial cables and screening help to reduce hum. Single point earthing helps too. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
I/O GCSE |
Shorthand for Input / Output. Usually an I/O Port. |
|
I/O Mapped A Level |
Input/output using an I/O port. The correct port is selected using the address bus. A control bus line is set in order to access I/O ports instead of memory addresses or the file registers. This is a type of multiplexing. |
|
IC GCSE |
See Integrated Circuit. |
|
Impedance AS Level |
This is the alternating current equivalent of resistance in a DC circuit. It is measured in Ohms and the letter Z often represents it. The maths is more complex because the current and voltage are often not in phase with each other. Impedance depends on the signal frequency. Antennas have the correct impedance, only at the design frequency. Vector triangles and Pythagoras are useful for impedance calculations. |
|
Impedance Matching A Level |
For maximum power transfer, the output impedance of one subsystem must be equal to the input impedance of the next. For example in wireless transmission, the antenna impedance and the feeder cable impedance must be the same. Common values are 50 and 75 Ohms. |
|
incf f, d A Level |
MPASM: (f) + 1 → d
The contents of register 'f' are incremented. |
|
Inductor / Inductance AS Level |
Energy is stored in an inductor in the form of a magnetic field. Inductors are coils of wire that act as electromagnets. XL = 2 π f L. Inductors create a Back EMF which opposes changes of current in the coil. Sudden current changes can create destructively large Back EMF voltages. |
|
Infinity GCSE |
In formulas, the symbol for infinity is ∞. This represents a very large number such as the input resistance of a field effect transistor. This is so high that it's hard to measure and impossible with a low cost multimeter. |
|
Information Signal GCSE |
This signal contains meaningful information. Voice, music and control data are three examples. This is sometimes called a baseband signal. See broadband. |
|
Input GCSE |
Most electronic systems have an input transducer used to measure a real-world parameter and convert the measurement into an electronic signal. Real world parameters include temperature, humidity, air pressure and many many more. In flowcharts, an input is shown with a slanting box. |
|
Input Impedance AS Level |
MOSFETs and non-inverting amplifiers have a very high input resistance. This property is most useful if the connected input device is not able to provide much current. |
|
Insulator GCSE |
Electrons are tightly bound to their parent atoms and they are not free to move. |
|
INTCON Register A Level |
Microcontrollers contain an INTERRUPT CONTROLLER Register. This contains pairs of flags and one global flag. ...IE Interrupt Enable flags - When set to one, interrupts are active - When set to zero, interrupts are disabled and ignored.
...F flags are set as follows
|
|
Integrated Circuit GCSE |
This is one wafer of silicon containing multiple devices manufactured into the silicon. ICs perform many useful functions and make modern electronics possible. Simple ICs contain dozens of components. The most complex ICs have over 7 billion transistors on one chip. (Written in 2016). |
|
Interfacing GCSE |
This is the circuitry needed to connect one subsystem to another. The simplest interface circuit is a piece of wire. Coupling capacitors are often needed to pass AC signals while blocking DC voltages. Interfacing can get quite complex. |
|
Interference GCSE |
Two signals or waves adding together. Often one signal is unwanted. Constructive interference causes the waves to add. Destructive interference causes waves to cancel out partially or fully. This causes the fading of radio signals. Unwanted interferance signals are sometimes called noise. |
|
Interrupts AS Level |
A signal to the processor suspends the current task, the return address and processor state are saved onto the stack, the interrupt code is executed and finally the processor resumes its previous state and task at the address retrieved from the stack. This technique is useful because the processor can get on with other work, only attending to the interrupt when necessary. See Polling. |
|
Intrinsic AS Level |
Intrinsic semiconductors are almost completely pure and do not conduct electricity well. Adding impurity atoms (dope) gives the useful properties needed to manufacture semiconductor devices or chips. |
|
Inverting GCSE |
The output is upside down relative to the input. Positive inputs become negative outputs. Logic ONE input gives logic ZERO output. |
|
iorlw k A Level |
MPASM: (W) .OR. k → W
The contents of the W register is OR’ed with the eight bit literal 'k'. |
|
IP A Level |
Internet Protocol. A set of rules allowing data packets to be routed to their destination. The IP rules ignore lost or damaged data. TCP deals with re-transmitting lost or damaged data. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Jitter A Level |
Pulses arriving too soon or late due to noise on the channel. Use a regenerator to clean up the noise and timing. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Karnaugh Map AS Level |
Special truth tables, useful for simplifying logic circuits or expressions. |
|
Kilo GCSE |
S.I. Units Prefix: 1000 103. Examples: Kilometres, kilogrammes, kilohms (NOT killer Ohms!) Remember to use a small "k". |
|
Kirchoff's Laws GCSE |
|
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Label AS Level |
In a microcontroller program, labels represent addresses. The addresses are calculated automatically by the Assembler program. Labels are used with GOTO, CALL and flag dependent skip instructions. The program counter is set to the address represented by the label. |
|
LAN GCSE |
A LAN is a local area network on a single site for a single organisation. Hosts are interconnected via switches. The LAN is connected to the cloud via a "gateway" router. Domestic broadband routers contain the gateway and switch functions in one box. |
|
LASER Diode GCSE |
These are used in fibre optic communications. The LASER can be switched extremely fast to encode high data rates onto a bright light beam. They are also used as pointers and for light shows. |
|
Latch GCSE |
D Type Flip Flops can be used. On the rising edge of the clock pulse, D is copied to the corresponding Q and the output data is stored until the next clock pulse. Latches can also be made from logic gates. The RS latch or bistable is a good example. |
|
Latency AS Level |
The time delay sending a signal through the transmitter, media, regenerators or routers and the receiver. This can often be heard when two TV sets are tuned into the same channel. There is an audio echo effect due to the different latency in the TV receivers. Latency is very noticeable on satellite links due to the huge distances the signal has to travel. It makes interactive robot control impossible on Mars, for example, because the time delay can be nearly 20 minutes! |
|
Layout Diagram AS Level |
This diagram shows the positioning of components on a circuit board. Circuit diagram symbols are often NOT used as the physical shape of the component is more important. These are often confused with circuit diagrams, system diagrams and flow charts. |
|
LCD GCSE |
Liquid Crystal Display. Very low power consumption. Needs a back-light in the dark. Easy to see in bright light. Some can display graphical shapes. Needs a microcontroller to drive it. |
|
LDR GCSE |
Light dependent resistor.
|
|
Leakage Current GCSE |
Ideal reverse biased diodes and capacitors have an infinite resistance. In real life they leak. Mostly this leakage current is so small it can be forgotten. Large timing capacitors take longer to charge or might never fully charge if there is too much leakage. |
|
LED GCSE |
Light emitting diode. A red LED has about 1.9 Volts across it. A blue LED might have 3.6 Volts across it. This is due to quantum physics. Blue photons are more energetic than red photons so a higher voltage is needed to make them. LED lighting is energy efficient and becoming common. |
|
LED Matrix Display AS Level |
7 x 5 array of LEDs. Any character can be displayed with limited resolution. Easy to see in the dark. Poor visibility in bright sunlight. High power consumption. A microcontroller is needed to drive it. 8 x 8 displays are available too. |
|
LF A Level |
The Low Frequency radio band is from 30 to 300kHz. It's also called Long Wave. |
|
Light Waves GCSE |
These are identical to radio waves but they have a much smaller wavelength. They travel through air or a vacuum at about 300 million metres per second. |
|
Lightning GCSE |
Lightning is a very short current burst. A side effect is intense bursts of radio energy that appears as noise in radio receivers. Direct hit lightning strikes are very dangerous. Near misses can destroy electronics. The energy in lightning causes surface heating and possibly fires. If a person is hit, their outer clothing can be superheated and should be removed as soon as possible. If their skin can be cooled quickly with water, this is a good idea. |
|
Limiting AS Level |
See Clipping and Saturation. Circuits can not normally produce an output larger than the power supply voltage. This is the limit. |
|
Line Regulation A Level |
Power supplies should produce a constant output voltage over a range of line input voltages. For example many lap-top power supplies and phone chargers will work correctly for any line voltage between 100 and 250 Volts. This means they can be used in most countries of the world without any worries. |
|
Linear GCSE |
Direct proportion. If you plotted a graph, the line would be straight. Linear amplifiers have minimal distortion. The output is proportional to the input (more voltage, current or power). |
|
Litz Wire A Level |
See Skin Effect. This wire is made from a lot of extra thin strands with a large surface area. It has a lower resistance to radio signals than normal wire. |
|
LM386 GCSE |
This is a widely used low cost, low power, audio power amplifier integrated circuit (IC) giving at least 0.25 Watts RMS output. |
|
LNB A Level |
The low noise block on a satellite dish. This uses a local oscillator and mixer to reduce the received satellite signals to a frequency low enough to be sent to the satellite TV using co-axial cable. Without this, expensive waveguide would have to be used to connect the dish to the TV. |
|
Load GCSE |
Loads have a resistance. Loudspeakers, motors and lamps are simple examples. A more complex example is the inverting amplifier which might have an input resistance of 47kΩ This input resistance acts as the load for the previous sub-system which must be designed to drive this. |
|
Load Regulation A Level |
Power supplies should maintain a constant output voltage, even if the output load current varies. Load regulation is a measure of how well a power supply manages to achieve this. Lack of smoothing can lead to an AC ripple in the DC output. The DC level might sag under heavy loads. Electronic voltage regulation helps to fix these problems. |
|
Logic GCSE |
Decision making circuits or Gates using simple rules like AND, OR, NAND, NOR, NOT, XOR and XNOR. Complex logic circuits (computers) can process text, maths, images, video and music. These are digital circuits processing noughts and ones. |
|
Logic (Combinational) AS Level |
Logic gate circuits without a clock or memory. The output changes immediately, responding to input changes. |
|
Logic (Sequential) AS Level |
Logic gate circuits with a clock and memory. The output changes on the clock signal. The output depends on the input and any stored information. |
|
Logic Gates GCSE |
See Logic. |
|
Loop GCSE |
This is a repeated electronic process. For example the temperature might be measured once per minute and different actions taken depending on the measurement. In flow charts, a loop is shown when the arrows double back to an earlier point in the flow chart. In programming GOTO often signifies a loop. |
|
Loudspeaker GCSE |
An output transducer which converts alternating audio currents into sound pressure waves in air. The most common speakers have an 8 Ohm resistance. |
|
Low GCSE |
An output voltage less than half the power supply voltage, often close to zero. Low may also be called False, Zero, No or Clear. See High. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Magnitude AS Level |
The size of a signal (ignoring polarity or direction). Amplifiers increase the magnitude of signals. |
|
Mains GCSE |
This is the 230 Volt 50 Hz alternating power available from sockets across Europe. In the USA it's 110 Volts at 60 Hz. |
|
Mains Plug GCSE |
|
|
Mark Space Ratio GCSE |
The On to OFF time of a square wave signal expressed as a ratio like 3:2 or 1.5. |
|
Maximum Power A Level |
For maximum power transfer from one subsystem to the next, the output resistance of the first should equal the input resistance of the next. This is particulatly improtant in radio frequency, small signal and antenna ciruits. A low output resistance can successfully drive a higher input resistance with reduced power transfer. A high output resistance can not normally drive a circuit with a low input resistance. Follower circuits are useful because of their high input resistance. |
|
Medium GCSE |
This is what the signal travels through. Examples: Free space ( air or vacuum ), copper cable, optical fibre. |
|
Mega GCSE |
S.I. Units Prefix: 1000000 106. Examples: Megahertz, Megabytes, Megohms. (NOT mega ohms !) Use a big "M". Small "m" means milli (a big mistake). |
|
Memory GCSE |
Memory types include ROM, RAM, Flash, Disk and Tape. |
|
Memory Mapped A Level |
A memory location is used for input/output to an external peripheral device. Compare this with I/O mapping. For example in the PIC16F88, PORTA resides at address 0x05 and could be used as a normal memory location. Doing this could make connected devices turn on or off. |
|
MF A Level |
The MF radio band is from 300 kHz to 3 MHz. It's also known as Medium Wave. |
|
Micro GCSE |
S.I. Units Prefix: 1 / 1000000 10-6 100 µF |
|
Microcontroller GCSE |
A self contained programmable chip containing all the necessary hardware such as the clock, memory, arithmetic and logic unit and the input and output ports. A system on a chip SoC with all the necessary parts on the same silicon wafer.
|
|
Microphone GCSE |
An input transducer that converts pressure waves in air into a proportional alternating voltage. |
|
Microprocessor A Level |
A central processing unit for a computer. It reads data, carries out arithmetic and logic and writes results. These chips usually have complex mathematical processing built in. Microcontrollers are much cheaper, simpler and lack complex maths. |
|
Microswitch GCSE |
Small reliable switches found in mice, game controllers and machinery. |
|
Mid-Range GCSE |
Audio frequencies needed for the human voice. The bare minimun is 300 Hz to 2700 Hz which sounds quite muffled. A more natural sound needs an upper limit of 4000 Hz. Small general purpose loudspeakers cover this range. See Bass and Treble. |
|
Milli GCSE |
S.I. Units Prefix: 1 / 1000 10-3 For example a length of 7 mm. |
|
Modulation GCSE |
This is the modification of a radio frequency carrier signal by the information signal.
|
|
Modulator GCSE |
This encodes a signal into a form suitable for transmission. For example Amplitude Modulation varies the amplitude of a carrier wave to carry speech or music. Sometimes it's called an encoder, especially for digital signals. See decoder, demodulator and detector. |
|
Monostable GCSE |
The 555 monostable circuit has one stable state and one unstable state. When triggered, it produces a single accurately timed pulse. T = 1.1 R C |
|
MOSFET GCSE |
Metal Oxide Semiconductor, Field Effect Transistor.
|
|
Motor GCSE |
An output transducer or actuator that converts electric power into (rotational or linear) movement.
|
|
movf f, d A Level |
MPASM: (f) → d
The contents of register 'f' is moved to a destination dependent upon the status of 'd'. |
|
movlw k A Level |
MPASM: k → W The eight bit literal 'k' is loaded into W register. The don’t cares will assemble as 0’s. |
|
movwf f A Level |
MPASM: (W) → f Move data from W register to register 'f''. |
|
Multimeter GCSE |
A meter which can be set to measure Volts, Amps, Ohms and sometimes other values depending on the model of meter. |
|
Multiplexer AS Level |
Many logic data inputs, for example 8. One logic output. A number of lines, for example 3, used to select which input is connected to the output. |
|
Multiplexing AS Level |
Sending two or more signals along one channel simultaneously.
|
|
Mutual Conductance AS Level |
gm = ΔID / ΔVG This applies to MOSFETs. Its the drain current change / the gate voltage change. It's measured in Siemens and historically in Mho (Ohm backwards). The value tells you how much the drain current will increase for a given gate voltage increase. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
N Type AS Level |
Silicon with four electrons in the outer shell is "doped" with Phosphorus, having five electrons. This leaves extra electrons where, in pure Silicon, only four would normally be expected. These extra electrons can migrate if a potential difference is applied. Electrons are negative and are attracted to positive potentials. |
|
NAND GCSE |
NAND Gate. The output is ZERO if all the inputs are ONE. |
|
Nano GCSE |
S.I. Units Prefix: 1 / 1000000000 10-9 47 nF |
|
Negative GCSE |
Electrons are negatively charged. Any material with more than the usual number of electrons is negatively charged. |
|
Neutron GCSE |
These are uncharged particles in the atomic nucleus. They have no effect on electronic circuits. |
|
NFC A Level |
Near Field Communication. This uses low power radio. The transmitters and receivers need to be less than 10 cm apart. Phones equiped with NFC can be used to pay for goods by placing the phone close to the payment terminal where an exchange of data takes place. Some store goods and animals are tagged with RFID tags to identify the product or animal. This uses a similar technology. |
|
Noise GCSE |
Unwanted signals. It can be a background hiss or cracks and bangs caused by lightning or the switching of industrial machinery. This is impulsive noise. Radio signals often suffer from noise due to unwanted signals leaking into the receiver. FM demodulators ignore the signal amplitude and therefore have better noise immunity then AM receivers. Warm conductors contain randomly vibrating atoms and electrons. If amplified, this appears as noise or a background hiss. The lowest noise circuits have to be cooled close to absolute zero. Don't confuse noise with distortion. |
|
NOP A Level |
MPASM: No operation No operation. |
|
NOR GCSE |
NOR Gate. The output is ONE if all the inputs are ZERO. |
|
NOT GCSE |
NOT Gate. The output is INVERTED. If the input is one, the output is zero. |
|
NPN AS Level |
A type of bipolar junction transistor with two layers of N type silicon and a middle layer of P type. See PNP. |
|
NTC GCSE |
Negative Temperature Coefficient. For example the thermistor is a temperature dependent resistor. The negative coefficient means that the resistance drops when the temperature increases. |
|
NVRAM AS Level |
Non Volatile RAM. The data is retained when the power is off. The data can be erased and new data recorded. |
|
Nybble or Nibble GCSE |
This is half a byte. 0101 1010 The low nybble is the right four bits in a byte. The high nibble is the left four bits in a byte. |
|
Nyquist Frequency AS Level |
When digitising, the sampling rate needs to be double the highest frequency being sampled. See Aliasing. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Octal GCSE |
This is an eight symbol number system whrere the you count like this: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 20, 21 - - - 74, 75, 76, 77, 100, 101 ... |
|
Ohm GCSE |
Ω - Resistance is measured in Ohms. More resistance results in less current. Resistance opposes the free flow of charge, usually electrons. |
|
Ohm's Law GCSE |
R = V / I V = I R I = V / R where R is the resistance, I is the current flowing and V is the potential difference across the device. |
|
OLED GCSE |
Organic Light Emitting Diode. These emit light when a current flows. They are used in phone, TV and other display screens. The quality and colour is excellent but the displays are still quite expensive. OLED displays can achieve a near perfect black colour, better that other disply types. OLED displays can be less bright than other types so they are harder to see in bright sunlight. |
|
ONE GCSE |
Logic one is any voltage above half the power supply voltage, often close to the power supply voltage. |
|
Open Loop GCSE |
A control system without negative feedback. See Closed Loop. |
|
Open Wire Feeder A Level |
Parallel wires used to connect a transmitter or receiver to an antenna. The wires are close together and the equal and opposite currents cancel out so the feeder does not pick up or radiate electromagnetic energy. |
|
Operational Amplifier GCSE |
Operational amplifiers have a very high open loop gain and near infinite input resistance. These properties make them useful in many circuits.
|
|
Optical Fibre A Level |
A two layer glass fibre used for communications by means of modulated light beams. The inner layer of glass has a high refractive index. The outer layer of glass has a lower refractive index. Light is trapped in the inner layer by total internal reflection. Optical fibres have a very high data bandwidth and they are more secure because they are so hard to tap. |
|
Optoelectronics GCSE |
Light used for electronic purposes such as carrying data. Components include LEDs, photodiodes, phototransistors, pin diodes, LASER diodes, display screens and fibre optic cables. CD and DVD disks store data optically. |
|
OR GCSE |
The output is zero if all the inputs are zero. |
|
Oscillator GCSE |
This is an astable circuit producing an AC output at a designed frequency. The output wave shape might be sine, square or saw tooth. Synthesizers can generate any wave shape. Oscillator circuits use positive feedback. |
|
Oscilloscope GCSE |
This measures voltage, period and wave shape. Frequencies can be calculated from F = 1 / P |
|
Output GCSE |
Electronic systems have one or more outputs. Sub-system outputs are fed to the next sub-system. The final sub-system output is fed to a transducer. Transducers include indicator lights, displays, sounders, loudspeakers, motors, solenoids, relays and many more devices. In flowcharts, an output is shown with a slanting box. |
|
Overflow GCSE |
There are too many bits to fit in the storage location. If you have a four bit counter, it can count from 0 to 15. It then overflows and goes back to zero. There is often an overflow output that allows more than one counter to be combined. In a microcontroller or computer, there is an overflow or carry flag which is set if some arithmetic causes an overflow. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
P N Junction (Diode) AS Level |
If electrons migrate towards holes, the electrons can fill the holes and a current can flow. If the polarity is reversed, the electrons migrate away from the holes leaving a DEPLETION ZONE with no free charge carriers and the current flow stops. Hence current can only flow in one direction. |
|
P Type AS Level |
Silicon with four electrons in the outer shell is "doped" with Boron, having only three. This leaves holes where, in pure Silicon, an electron would normally be expected. These holes can migrate if a potential difference is applied. Holes are Positive and are attracted to negative potentials. |
|
Packet Extras Non Exam |
A packet contains...
|
|
Packet Switching Extras Non Exam |
Almost all networks are linked via ROUTERS which send packets towards their destination.
|
|
PAM A Level |
Pulse Amplitude Modulation. The amplitude of fixed width pulses is modified in proportion to the sampled level of the information signal. |
|
Parallel GCSE |
Components wired side by side.
|
|
Parallel Data A Level |
It travels on a multi-wire bus. The groups of bits travel side by side. Parallel data is faster than serial because of the multiple wires. In practice serial transmission has become so fast that nearly all data is serially transmitted apart from the parallel buses inside computers, microprocessors and microcontrollers. |
|
Parallel Port A Level |
PORTA, PORTB and PORTC are eight bit parallel ports. The eight lines can be configured as inputs or outputs by setting TRISA, TRISB or TRISC. |
|
Passive GCSE |
Components like capacitors, resistors, switches and inductors. These are usually NOT semiconductor devices. See Active. |
|
Passive Filter A Level |
This uses only resistor/s and capacitor/s and less often inductor/s. See Filter. |
|
PCM A Level |
Pulse Code Modulation. The information signal is sampled and converted into binary numbers. The binary is transmitted as a stream of pulses. |
|
Peak GCSE |
The highest voltage point on a wave. Peak Voltage = 1.4 x VRMS |
|
Period GCSE |
The duration of one complete cycle of a wave. Period = 1 / Frequency. |
|
Phase A Level |
Compares the position of waves or rotating systems in space or time. Phase is measured in radians or degrees of angle. |
|
Photodiode GCSE |
A diode that is sensitive to light. In the dark, a reverse biased diode passes very little current. Photons of light dislodge electrons and increase the leakage current. |
|
Photosensitive GCSE |
Any component that responds to light or infra-red or ultra-violet. LDR, Photodiode, Phototransistor, PIN Diode, CCD camera sensor, CMOS camera sensor. There are many more. |
|
PIC GCSE |
Programmable Integrated Circuit. See Microcontroller and AVR. |
|
Pico GCSE |
S.I. Units Prefix: 1 / 1000000000000 10-12 Capacitance = 33 pF |
|
Piezoelectric Effect GCSE |
Substances like quartz deform if a potential difference is applied across the surfaces. This can be used to make sounders, tweeters, crystals for accurate timing in oscillators and for high quality filters. This process also works in reverse, allowing movements to be converted into a voltage. Some mirophones and ultrasound sensors use this effect. |
|
PIN Diode A Level |
This is a very fast light sensing transducer used for fibre optic communication systems with high data rates. |
|
PISO AS Level |
Parallel In, Serial Out. Shift registers are used to convert between serial and parallel data streams. USB is an example of serial data. Data and Address Buses inside computers are mostly parallel. |
|
Plug Wiring GCSE |
|
|
PNP GCSE |
A type of bipolar junction transistor with two layers of P type silicon and a middle layer of N type. See NPN. |
|
Polarisation A Level |
Electromagnetic radiation is polarised. This is the angle at which the electric field is oriented. Mostly this is random, horizontal or vertical but circular polarisation is possible too. Antennas need to be polarised to match the radiation they need to reveive or transmit. |
|
Polarity GCSE |
Correctly identifying and connecting the + and - connections. For some components this is critical. For others, they can be connected either way round. |
|
Polling A Level |
Repeatedly reading a port whether the data has changed or not. This is not the most efficient way to use a processor's resources. See Interrupts. |
|
PORTA, PORTB GCSE |
Ports are used for data input (reading) and output (writing). |
|
Positive GCSE |
In the nucleus of an atom, the protons are positively charged. Normally this charge is exactly balanced by the correct number of electrons and the material is neutral or not charged. If some electrons are removed, a net positive charge remains. |
|
Potential GCSE |
A voltage measured relative to Earth or Ground. |
|
Potential Difference GCSE |
A voltage measured across a circuit or component ignoring Earth or Ground connections. |
|
Potentiometer GCSE |
A variable resistor. A slider moves along a resistive track altering the resistance from 0 to 100% of the value of the component. It's often used as a volume control of for changing the timing in an RC circuit. |
|
Power GCSE |
|
|
Power Supply GCSE |
This usually refers to a 110V / 230V mains powered box that produces low voltage DC suitable for electronic circuits. The term is also used for cells, batteries, photocells and other power sources. |
|
PPM A Level |
Pulse Position Modulation. The position (in time) of pulses is modified in proportion to the sampled level of the information signal. The amplitude and width of the pulses is fixed. |
|
Process GCSE |
Most electronic systems contain a process. This could be an amplifier, a comparator, a timer, an astable oscillator, one or more logic gates or a microcontroller chip capable of performing computations. In flowcharts, a process is shown as a rectangle. |
|
Program GCSE |
A set of instructions to carry out a task understood by the microcontroller or microprocessor. |
|
Protocol A Level |
A set of rules which allows successful communication to take place. Examples include TCP, IP, Ethernet, HTTP, HTTPS and FTP. |
|
Proton GCSE |
A positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom. In electrically neutral matter, the charge on each proton is cancelled out by a nearby negative electron. |
|
Pulse GCSE |
This is usually a square wave toggling on and off again. |
|
Push Pull A Level |
A type of amplifier that uses two MOSFETs or Junction Transistors. One amplifies the positive half of the signal. The other amplifies the negative half. |
|
PWM A Level |
Pulse Width Modulation. The width of fixed amplitude pulses is modified in proportion to the sampled level of the information signal. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Q Factor A Level |
The quality factor of a tuned circuit. Q = f / ( ΔF ) where f is the resonant frequency and ΔF is the bandwidth of the tuned circuit. |
|
QAM Extras Non Exam |
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation. The phase and amplitide of the carrier are modulated. This allows 4, 8, 16 or more bits to be encoded in each symbol or transmission interval (equivalent to the baud rate). |
|
Quantised AS Level |
The action of an A to D converter converting an analogue signal with an infinite range of values into a digital signal with, for example, 256 levels or quanta. This process leads to a small loss of signal accuracy called quantisation error. |
|
Quantum Dot GCSE |
Quantum dot devices are so small that their behaviour is controlled by quantum physics. Quantum dots can be made to emit light with the colour depending on the size of the dot. Future display screens might be based on quantum dots giving much improved picture quality, possibly even better than OLED. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Radio Frequency (RF) GCSE |
Frequencies above about 50kHz are called radio frequencies because it's possible to transmit them if they are fed into a suitable antenna. |
|
Radio Spectrum GCSE |
The radio spectrum ranging from VLF up to UHF, EHF, Infra-Red, Visible, Ultra-Violet, X-Rays and beyond. |
|
Radio Waves GCSE |
These are electromagnetic waves. They travel through air or a vacuum at 300 million metres per second. |
|
RAM GCSE |
Random Access Memory. This is typical computer memory. The data is lost if the power is turned off. This is known as VOLATILE memory. |
|
Reactance A Level |
The equivalent of resistance for capacitors and inductors in alternating current circuits. Measured in Ohms. It depends on frequency. |
|
Read GCSE |
Data is copied from memory or an I/O port into the processor. See Write. |
|
Receiver A Level |
|
|
Rectifier GCSE |
A diode used to convert AC into DC. This process is called rectification. |
|
Rectifier Half-wave GCSE |
Power supplies with only one diode rectify only half the AC cycle. |
|
Redundancy A Level |
Duplicated hardware to make it more reliable or fault tolerant. Multiple network links. Backup power supplies. RAID disks. |
|
Reed Switch GCSE |
This is a magnetically operated switch enclosed inside a glass tube. If there is a magnet near the tube, the switch contacts are attracted and the switch turns on. A simple intruder alarm can be made by placing the magnet in a door and the switch in the door frame. When the door is opened, the switch turns off and the alarm sounds. |
|
Regenerator A Level |
A Schmitt trigger circuit used restore logic levels and remove noise from a digital signal. It might use other techniques to remove timing errors or jitter. See Repeater. |
|
Register A Level |
A storage location, often inside a microcontroller or microprocessor. Microcontroller registers include ...
|
|
Relative Position A Level |
The amount of movement is known but not the absolute or exact position. |
|
Relay GCSE |
A small current in the coil of the electromagnetic relay creates a magnetic field which attracts a lever which switches over the relay switch contacts. In this way large currents can be switched. Relays lack reliability due to the moving parts. Relays can switch high voltages and alternating currents. |
|
Repeater A Level |
This amplifies the analogue or digital signal including any noise and passes the amplified signal on. No clean-up is attempted. This is OK if the signal is already clean enough. See Regenerator. |
|
Reset GCSE |
Restore a circuit to its "Switch On State". |
|
Residual Current Device GCSE |
This acts like a fuse and shuts off the circuit if the current is too big. The second advantage is shutting off the circuit if the current is leaking on a fault path. This could include a person being electrocuted so the RCD is a really useful safety device. |
|
Resistance GCSE |
Resistance opposes the free flow of current or electrons. It can be calculated using Ohm's Law. |
|
Resistor GCSE |
A component with a known amount of resistance which is constant over a wide range of temperatures and frequencies.
|
|
Resolution AS Level |
The smallest measurable step or the step size. |
|
Resonance A Level |
A natural frequency of oscillation where the amplitude becomes much larger than at other frequencies. Radio tuning relies on this effect in tuned circuits. |
|
retfie A Level |
MPASM: TOS → PC 1 → GIE
Description: Return from Interrupt. |
|
return A Level |
MPASM: TOS → PC
Return from subroutine.
The stack is POPed and the top of the stack (TOS) is loaded into the program counter. This is a two cycle instruction.
|
|
Reverse Bias GCSE |
The current or voltage is in the opposite direction to that normally expected. For example Zener diodes are used in reverse bias and the current flows in the opposite direction to that in a normal diode. Reverse biased electrolytic capacitors could explode. |
|
RF GCSE |
See Radio Frequency. |
|
RFID A Level |
A radio technology where the RFID chip transmits data when activated by the energy from a nearby transmitter. The RFID chip does not normally have its own power source. Pets and farm animals are "chipped" for easier identification. Some retail organisations use RFID chips instead of barcodes. |
|
RISC AS Level |
Reduced Instruction Set Computing (or chip) usually using the Harvard architecture. The microcontroller makes do with a few, very high performance instructions. See CISC. |
|
RMS Current AS Level |
For sine wave signals RMS current = Peak Current / √2 = Peak Current x 0.707 |
|
RMS Power AS Level |
For sine wave signals RMS power = Peak Power / 2 |
|
RMS Voltage AS Level |
For sine wave signals RMS voltage = Peak Voltage / √2 = Peak Voltage x 0.7 |
|
Robot GCSE |
A robot is a machine but unlike a conventional machine, it can be re-programmed to perform new tasks. |
|
ROM GCSE |
Read Only Memory. This is computer/microcontroller memory. The data can not be altered and is not lost if the power is turned off. This is known as NON-VOLATILE memory. It is used to store essential programs required for the operation of the chip. |
|
Router GCSE |
Small local networks are interconnected via ROUTERS to make a wide area network such as the Internet. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Sample and Hold AS Level |
A circuit which accurately stores an analogue voltage for a short period. It's needed in A to D converters to maintain a steady value while the conversion is taking place. |
|
Sampling GCSE |
Repeatedly measuring an analogue signal and converting it into digital. The sampling must occur at at least double the frequency of the highest frequency being sampled. |
|
Saturation GCSE |
Once a transistor, MOSFET or amplifier is 100% switched on, increasing the input has no further effect. This is saturation. Seeclipping. |
|
Schmitt Trigger GCSE |
|
|
Screen/screening GCSE |
Metal or foil sheets or boxes are used to screen circuits to prevent wanted signals getting out and unwanted signals getting in. Poor screening is a common problem, most often noticed when a mobile phone interferes with an audio circuit. Co-axial cable is screened with an outer woven braid or foil layer. |
|
Selectivity GCSE |
This is a measure of the ability of a radio to select the wanted frequency or station and to reject all others. |
|
Semiconductor GCSE |
Pure (intrinsic) semiconductors like silicon do not conduct electricity at room temperature. By adding impurities like Boron or Phosphorus, the electronic properties can be controlled and the whole range of semiconductor devices can be manufactured. |
|
Sensitivity GCSE |
This is a measure of the ability of a radio receiver to pick up weak signals. |
|
Sensor GCSE |
An input transducer used for detecting or sensing signals from the environment and converting them into a proportional voltage or current. |
|
Sequential Logic GCSE |
Logic circuits with a clock and memory. The outputs change in time with the clock. |
|
Serial Data A Level |
Bits are transmitted down one wire (or other channel) one after another. USB is a very common serial data interface. See Parallel.
|
|
Series GCSE |
Components connected end to end.
|
|
Servo GCSE |
A motor with 90o of rotation. The angle is controlled with a stream of pulses between 1 and 2 ms wide. Other angles are available. |
|
Set GCSE |
The signal/output goes high or becomes one. See Clear. |
|
Seven Segment Display GCSE |
It's only possible to display digits and a very few letters. Simple drive logic.
|
|
Shaft Encoder A Level |
This is used to measure the rotation of a shaft.
|
|
Shift Register A Level |
This uses D Type Flip Flops. On the rising edge of the clock pulse, D is copied to Q and all the data moves one place to the right in the shift register. This circuit is useful for converting serial data into parallel and also parallel data into serial. Pseudo-random numbers can be generated. Pulses can be delayed. Combination lock circuits are possible. |
|
Shock (electric) GCSE |
Muscular spasms, burns, difficulty breathing, heart stops.
|
|
Short / Short Circuit GCSE |
A wiring error that causes the circuit to get hot and in extreme cases catch fire. Connecting a wire across the battery or power supply creates a short. A common circuit diagram howler is to short the power lines. |
|
SI Units GCSE |
The International System of Units. When calculating always use whole SI units like Volts, Amps, or Ohms. When working with millivolts or kilohms, always do the right conversion before calculating. |
|
Sidebands A Level |
When a carrier is modulated, sidebands are always produced. The width of the sidebands is at least equal to the bandwidth of the information signal being transmitted and double for AM or even more for FM. |
|
Signal GCSE |
This is an electric current, voltage, optical or audio pulse that represents useful information such as speech, music, measurement or control data. In nature there are many other types of signal such as chemical messages delivered by hormones or pheromones. |
|
Signal Generator GCSE |
This produces an alternating signal at a known frequency and voltage. It is used for testing circuits. Most signal generators produce a choice of wave shapes including sine, square and saw tooth shapes. |
|
Signal to Noise Ratio A Level |
Measured in dB. A big number indicates lots of signal and not much noise. |
|
Silicon GCSE |
The most widely used semiconductor material. Do not confuse with silicone which is used for breast implants, water proofing and sealing baths or sinks. |
|
Silicone GCSE |
A widely used rubbery material used for water proofing, bath sealant and breast implants. Do not confuse with silicon! |
|
Simplex A Level |
One way / single direction communication such as radio broadcasting. See Duplex. |
|
Sine Wave AS Level |
A pure signal containing only one frequency. |
|
Sink GCSE |
A low output capable of supplying current up to a limit specified in the component data sheet. See source. |
|
SIPO AS Level |
Serial In, Parallel Out. Shift registers are used to convert between serial and parallel data streams. USB is an example of serial data. Data and Address Buses inside computers are mostly parallel. |
|
Skin Effect A Level |
Radio frequency (RF) currents flow, only in the surface of the conductor. For better performance, conductors with a large surface area are a good idea. Tubes are good and and also special wire with a very large number of thin strands called Litz Wire. High current RF conductors are silver plated to reduce resistive energy loss. RF electric shocks don't penetrate into the body. Instead the skin surface gets burned - not nice. Lightning strikes have a short duration and are a type of RF so they also cause skin burns. |
|
Skin Resistance GCSE |
The resistance of wet human skin is much lower so electric shocks are more dangerous if your skin is wet. This makes bathrooms and kitchens more dangerous for electrical safety. |
|
Slew Rate AS Level |
This is the fastest rate (measured in volts per microsecond) at which the output of a device can rise and fall. If an op-amp input goes high, the output might take 12 microseconds to catch up. |
|
Slew Rate Distortion AS Level |
If the input of an amplifier is rising or falling faster then the output slew rate, distortion results. The only way to cure this distortion is to use a faster device. For a clean sine wave with frequency f, the minimum slew rate = 2 π f Vp where Vp is the peak voltage. |
|
Smart Card GCSE |
It is the size of a credit card and it contains a microcontroller, ROM, RAM and NVRAM. It connects to a card reader using metallic pads printed onto the card. |
|
Smoothing GCSE |
Large capacitors are used to smooth out the voltage ripple in the DC outut of power supplies. |
|
SoC GCSE |
System of a Chip. Microcontrollers have all the required hardware on a single chip. |
|
Software GCSE |
This is stored on computer disks, pen drives, CDs, DVDs etc. Software is the programs and data needed to make computers work. Software must be backed up in case there is a hardware failure that causes the software to be lost. See harware. |
|
Solenoid GCSE |
An electromagnetic actuator providing linear movement. Turning on the magnet makes the mechanism move. |
|
Soliton A Level |
A special pulse shape that travels without dispersion. These are being researched because they could enable higher communications data rates. |
|
Sound Waves GCSE |
These are pressure waves in air. They travel at about 330 metres per second. This is roughly one million times slower than light waves. |
|
Sounder GCSE |
This transducer produces sound from an alternating signal such as the 555 astable output. See Buzzer. |
|
Source GCSE |
A high output capable of supplying current up to a limit specified in the component data sheet. See sink. |
|
Source Follower AS Level |
A useful buffer circuit with
|
|
Speaker GCSE |
See Loudspeaker. |
|
Spectrum AS Level |
A range of frequencies. The audio spectrum is from 20 Hz to 20000 Hz. The radio spectrum is sub-divided into bands like LF, MF, HF and VHF. |
|
Spectrum Plot A Level |
A graphical representation of voltage or power plotted on the Y axis against frequency plotted on the X axis. |
|
Speed AS Level |
Examples include the speed of light or the speed of sound. It is WRONG to refer to the speed of a data link. Use Bandwidth or Bit Rate instead. In a faster data link, the data takes just as long to arrive unless faster than light communication has just been invented. However more bits per second can be transmitted and received. |
|
Square Waves GCSE |
These are produced by all digital logic circuits and astable circuits like the 555 astable. The signal switches suddenly between the high and low levels producing the square wave shape. |
|
Stack A Level |
Memory used for saving the return address when a processor performs a sub-routine or interrupt. See CALL and RETFIE. |
|
Status Register A Level |
Microcontrollers contain a STATUS Register. This contains FLAGS. The flags are set to ONE under certain conditions.
|
|
Step Index A Level |
A type of optical fibre with two separate layers of glass with different refractive indexes. The more expensive single mode fibre is better. |
|
Stepper Motor GCSE |
Moves in precise angular steps. Excellent for robotic position control. More complex driver circuits are needed. Large or fast stepper motors can't easily be made. |
|
Sub-systems GCSE |
These are self contained electronic circuits that perform a useful function. An example is a voltage divider made from two resistors. This produces a known output voltage and the circuit can't be sub-divided any further. Another example is a 555 monostable. This sub-system can be sub-divided into smaller sub-systems like the RC timing circuit, comparators and RS Flip Flop. |
|
sublw k A Level |
MPASM: k - (W) → W
The W register is subtracted (2’s complement method) from the eight bit literal 'k'. |
|
Subroutine AS Level |
A small re-usable block of code, often from a library of useful subroutines. Subroutines allow larger programs to be modularised. They avoid having to write the same code more than once. In other programming languages they might be called procedures, functions or methods. |
|
Summing DAC AS Level |
A summing amplifier with input resistors values in the 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 pattern. This circuit is used to convert a binary number digital value back into an equivalent analogue voltage. |
|
Switch A Level |
A device that learns the MAC addresses of hosts on the local network and correctly forwards frames to the right device. They commonly have 4 to 32 ports for local computers or hosts. |
|
Switch GCSE |
A resistive transducer with a resistance of zero or infinity Ohms. Switches are digital transducers.
|
|
Synchronous A Level |
Signalling where the sender and receiver use the same clock signal or the clock signal is included in the transmission. Input pulses always arrive synchronised to the clock signal. |
|
System GCSE |
The complete electronic system built up from simpler sub-systems. |
|
System Diagram GCSE |
Labelled rectangular boxes joined with arrows. The boxes show how a system is divided up into sub-systems. The arrows show the information signals between the sub-systems. These are often confused with circuit diagrams, layout diagrams and flow charts. |
|
System Synthesis GCSE |
This is the idea of dividing large complex systems into smaller, easy to understand, easy to test, sub-systems. System diagrams are used to describe the sub-systems needed for a full system. It's common to buy pre-built subsystems to solve common problems. Most integrated circuits fit this category. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
TCP A Level |
Transmission Control Protocol. A set of rules allowing internet data to be acknowledged, put into the correct sequence and re-transmitted if necessary. TCP uses IP to send the actual packets. |
|
Telemetry A Level |
Scientific, engineering or medical measurement values transmitted, usually by radio. |
|
Tera GCSE |
S.I. Units Prefix: 1000000000000 1012 A 2 TB disk terabytes |
|
Thermal Cut Out GCSE |
A safety device using a bimetal strip which bends when heated. If the circuit current is too big, the strip gets hot and bends so much that it shuts off the faulty circuit. |
|
Thermistor GCSE |
A temperature dependent resistor.
|
|
Thevenin AS Level |
Multiple voltage sources and linear components like resistors can be simlpified to a single resistor in series with a single voltage source. |
|
Thyristor A Level |
A three pin Silicon Controlled Rectifier ( SCR ). A short gate current pulse turns on the device. It latches and remains on.
|
|
Tilt Switch GCSE |
The switch contains a bead of mercury. When tilted, the mercury flows and joins the switch contacts. Non-mercury tilt switches are available. |
|
Time Slices A Level |
Time is shared out between many devices using a single time division multiplexing channel. |
|
Timing Circuit GCSE |
Resistor Capacitor Timing Circuits T50% = 0.69 RC T63% charging = RC T37% discharging = RC T100% = 5 RC. |
|
Timing Diagram GCSE |
A diagram showing how the logic states (zero or one) of a circuit change with time. |
|
Tolerance GCSE |
The manufacturing accuracy of components. Resistors come in 1, 2, 5 and 10% tolerance. Capacitors can be as poor as 20% tolerance. |
|
Transducer GCSE |
This converts energy from one form into another. For example a microphone converts sound waves into an alternating voltage proportional to the air pressure of the sound wave. This is an input transducer. The loudspeaker is an output transducer and it converts an alternating current into pressure waves in the air. |
|
Transfer GCSE |
|
|
Transformer GCSE |
A device used to step up or step down alternating voltages and currents. The transformer consists of two coils magnetically coupled together. Mains transformers have an iron core that greatly increases the magnetic coupling. |
|
Transistor GCSE |
Base, Collector, Emitter
|
|
Transition Gate GCSE |
Clocked gates like D Type Flip Flops respond when the clock signal makes a TRANSITION. The 4013 flip flop and the 4017 decade counter chips are activated by the rising edges of the clock signal. |
|
Transmitter A Level |
A transmitter sub-system is an amplifier used to increase the power of the signal from the modulator to a level, high enough to feed to the antenna or fibre. The term is also used to include all the sub-systems including the carrier generator and modulator. |
|
Treble GCSE |
Audio frequencies above 2000 Hz. High quality loudspeakers have a tweeter driver for treble frequencies. See Bass and Mid Range. |
|
Triac A Level |
Power switching of DC and AC. This is effectively two thyristors back to back. The properties are bi-directional. Waste heat is less problematic. Low cost.
|
|
TRISA, TRISB etc GCSE |
These are data direction registers. PORTA, B and C carry the data. TRISA, B and C are used to determine which port pins are inputs or outputs. Tristate logic makes this possible. |
|
Tristate A Level |
Tristate logic allows multiple devices to share one bus. All the devices except for one are disconnected. The one that is connected can set the bus lines to zero or one. The three logic states are Zero, One and Disconnected (or high impedance). The address bus is used to uniquely select a single tristate device. |
|
Truth Table GCSE |
Truth tables containing zeros and ones describe the all the possible inputs and the outputs of a logic circuit. |
|
Tuned Circuit A Level |
A capacitor (often variable) and an inductor (coil) used to select a single frequency. This provides selectivity in a receiver and controls the transmission frequency in a transmitter. | |
Tuning A Level |
Adjusting a tuned circuit or other filter to the wanted frequency. |
|
Twisted Pair Cable A Level |
This cable is widely used in computer networks. The twists in the pairs of conductors greatly reduce crosstalk. The twists are not constant throughout the length of the cable and are carefully designed to allow the maximum data bandwidth. Equal and opposite currents in the pairs of conductors cause magnetic coupling effects to cancel out. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
UDP A Level |
User Datagram Protocol is used for audio and video streaming. There are no acknowledgements and lost data shows up as gaps in the audio or momentarily frozen or poorer quality images. |
|
UHF A Level |
Ultra-high Frequency. The UHF radio band is from 300 to 3000 MHz. Broadcast TV, Mobile Phones, WiFi. |
|
Uplink A Level |
A radio signal from the Earth up to a satellite. Also a signal from a mobile phone up to the cell base station. See Downlink. |
|
USB A Level |
A half duplex serial data connecting cable used with computers. Ground, +5Volts, D+ and D-. The Data lines are twisted together to reduce crosstalk and interference into or out of the cable. USB3 supports Full Duplex. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Vacuo or Vacuum A Level |
The vacuum of free space. This is a transmission medium for electromagnetic radiation. |
|
VHF A Level |
Very High Frequency. The VHF radio band is from 30 to 300 MHz. FM is used in the 88 to 108 MHz broadcast band. DAB Radio uses frequencies around 220 MHz. |
|
Virtual Earth AS Level |
Operational amplifiers have a very high open loop gain. If the output is a few volts, the inverting input will be a few microvolts. This is so close to zero, it's called a virtual earth. This works as long as the amplifier is not saturated or limiting. |
|
Volatile GCSE |
Volatile memory "forgets" when the power is turned off. Non-volatile memory retains its contents with the power turned off. RAM is volatile. ROM, flash, CD ROM, DVD ROM and hard disk memory are all non-volatile. |
|
Volt / Voltage GCSE |
Positive volts attract electrons. Negative volts repel electrons. If the electrons are free to move (in a conductor), the volts will cause the electron movement or current. If there are two voltages giving a potential difference and if there is a complete circuit, current will flow. |
|
Voltage Divider GCSE |
The voltage is divided up in the same ratio as the resistors.
|
|
Voltage Regulator GCSE |
A three pin device that provides a stable DC Voltage output from an unsteady DC supply. |
|
Voltmeter GCSE |
Connect it in parallel with the component being measured. No current flows through an ideal voltmeter. |
|
Von Neumann AS Level |
The three bus architecture of a microprocessor. Instructions and data are fetched in two separate steps. Compare this with the Harvard architecture. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
W AS Level |
W is the Working Register in a microcontroller. Arithmetic and logic results end up in the W register. |
|
WAN A Level |
A wide area network between multiple LAN sites, interconnected via routers and via multiple routes. The Internet is the ultimate WAN. |
|
Watt GCSE |
Power is measured in Watts. P = I V P = V2 / R P = I2 R |
|
Wave Band A Level |
|
|
Waveguide Extras Non Exam |
Expensive metal pipes used to carry radio waves with wavelengths measured in millimetres or a few centimetres. Normal cables don't work for such short wavelength signals. |
|
Wavelength GCSE |
The length of a complete cycle of a wave wave. λ = C / F where
|
|
Wetware GCSE |
Originally a joke about hardware and software, wetware is now commonly used to refer to human or animal brains used to process information. "The problem's in the wetware. Someone needs to read the manual." |
|
WiFi GCSE |
A radio-wave wireless technology used to connect computing devices. No cables are needed. It's less secure than a wired connection. |
|
Write GCSE |
Data is copied from the processor (to the memory or an output port) See Read. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
XNOR GCSE |
XNOR Gate. Equal inputs give ONE. Non-equal inputs give ZERO. |
|
XOR GCSE |
XOR Gate. Equal inputs give ZERO. Non-equal inputs give ONE. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Yagi Extras Non Exam |
A directional antenna used for radio transmitting and receiving. It's useful because the energy is transmitted directionally. This improves the efficiency and reduces the chance of unwanted interference from other radio stations. |
|
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
||
Zener Diode GCSE |
This diode is used in reverse bias breakdown mode to provide an accurate reference voltage. |
|
ZERO GCSE |
Logic zero is any voltage below half the power supply voltage, often close to zero Volts. |
|
Contact, Copyright, Cookies and Legalities: C Neil Bauers - reviseOmatic V4 - © 2016 to 2025
Hosted at Akamai Cloud - London
Please report website problems to Neil