

Fuse |
|
To gain access to revision questions, please sign up and log in.
A fuse is a safety device. It contains a thin wire which is designed to melt when too large a current passes through it. The fuse prevents too much current which could otherwise cause overheating and possibly fire.

Note the 200,000 Amp fuse in the image. This probably came from a power generating station.
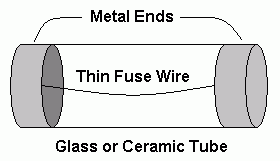
Fuses are used to protect circuits by preventing large currents from flowing. In the UK, power connectors for devices like kettles and fan heaters use a 13 Amp fuse. If more than 13 amps pass through the circuit, the fuse wire melts and the circuit is turned off. This protects the other wiring from overheating and possibly causing a fire. Smaller fuses (three amp) are used for low power appliances like table lights and radios. Always use the smallest possible fuse that will not fail under normal (or switch on) current operating conditions.
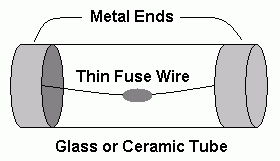
This is similar to a normal fuse but the metal blob prevents the wire heating and melting so quickly. This is useful if the circuit has a switch-on surge current.
reviseOmatic V3 Contacts, ©, Cookies, Data Protection and Disclaimers Hosted at linode.com, London