WANTED: Individual or team to take over this project. I'm in my 70's and want to put my feet up. Contact details in footer.
| A Level Instrumentation Bridge Circuits >Difference Amplifier< Position Sensing |
Instrumentation Difference Amplifier |
|
The difference amplifier (Differential Amplifier) amplifies V+ - V-. For best results, the resistors should be matched or trimmers should be used to perfectly match them.
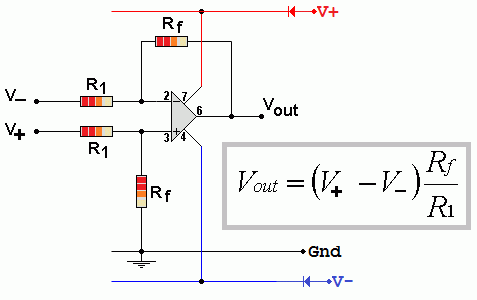
The input resistance between the two inputs is equal to 2 x R1.
To prevent sensor signal loss, these input resistors should be 10 to 100 times larger than the sensor resistors.
If this input resistance is too low to be connected to input sensors, place a voltage follower before each input.
This raises the input resistance close to infinity and improves accuracy.
Differential Amplifiers are often used when there is likely to be noise on the input channels. The signal is amplified and the noise is cancelled out. This happens with many transducers that have a small output. Strain gauges are a good example.
Another common example is when a microphone with a long connecting wire is plugged into a public address amplifier. A balanced microphone with two signal wires and a separate ground wire is connected to the inputs.
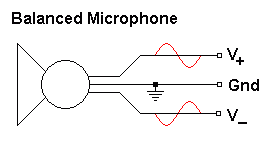
Microphone + Noise Example
A special balanced microphone is needed for this to work.
When one microphone wire goes positive, the other wire goes negative by an equal amount. If the microphone voltage is V, the amplifier output is V - (- V) = 2V.
If there is noise N, the amplifier noise output is N - N = 0. Thus the noise is cancelled. This relies on the fact that the noise will be picked up equally by both inputs whereas the microphone signal is opposite on each input wire.
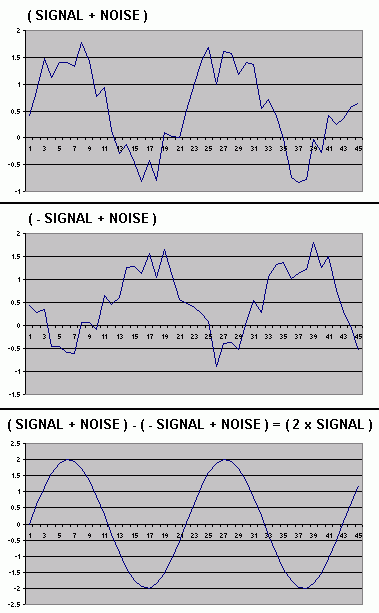
The charts show two noisy signals. When subtracted from each other, the clean signal remains and the noise is cancelled out.
- These charts were produced using an Excel spreadsheet.
- The signal was produced using the Excel sine function.
- The noise was produced using the Excel random number function.
- If you edit an empty cell in the spreadsheet, the random data gets updated but the cleaned signal stays clean.
Subject Name Level Topic Name Question Heading First Name Last Name Class ID User ID
|
Q: qNum of last_q Q ID: Question ID Score: num correct/num attempts Date Done
|
Question Text
image url
Help Link
Add Delete Clone Edit Hardness
Contact, Copyright, Cookies and Legalities: C Neil Bauers - reviseOmatic V4 - © 2016 to 2025
Hosted at Akamai Cloud - London
Please report website problems to Neil