| AS Level Timing >RC Timing< Schmitt NOT Astable |
Timing RC Timing |
|
In addition to the basic timing concepts needed for all subject levels, AS and A Level students need a more mathematical approach involving logarithmic and exponential maths. This involves the ln button on your calculator that you may not have used before. The inverse button function is the ex exponential. Some calculators have separate buttons for these functions. You'll also need to learn the difference between the - button and the ± button. In everyday English you may have heard of exponential growth or decay. That's the ex button on your calculator.
Formula |
|
Time Constant = R C |
Charging: T63% = R C T50% = 0.69 R C T100% = 5 R C Discharging: T37% = R C T50% = 0.69 R C T0% = 5 R C 555 Monostable: T66.6% = 1.1 R C |
Charging Volts |
VC = V0 ( 1 - e - t / RC) If you know the time, you can calculate the volts. |
Discharging Volts |
VC = V0 e - t / RC If you know the time, you can calculate the volts. |
Charging Time |
t = -RC ln( 1 - VC / V0 ) If you know the volts, you can calculate the time. |
Discharging Time |
t = -RC ln( VC / V0 ) If you know the volts, you can calculate the time. |
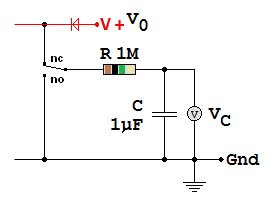
For this circuit, the time constant T = R C = 1 x 106 x 1 x 10-6 = 1 Second
For an uncharged capacitor, after a time t, the capacitor voltage VC = V0 ( 1 - e - t / RC)
This is tricky to work out with a calculator. You could attempt it using loads of brackets.
Or you could break it down into smaller safer calculations.
Here is a test case. After 0.69 seconds, the circuit above should have charged to 50% of V0. If V0 is 100 Volts, the answer should be very close to 50V.
Subject Name Level Topic Name Question Heading First Name Last Name Class ID User ID
|
Q: qNum of last_q Q ID: Question ID Score: num correct/num attempts Date Done
|
Question Text
image url
Help Link
Add Delete Clone Edit Hardness
Contact, Copyright, Cookies and Legalities: C Neil Bauers - reviseOmatic V4 - © 2016/17
Hosted at linode.com - London
Please report website problems to Neil