WANTED: Individual or team to take over this project. I'm in my 70's and want to put my feet up. Contact details in footer.
| A Level >AC Circuits< Active Filters Passive Filters Tuned Circuits |
AC Circuits |
|
At high prequencies, capacitors pass currents as easliy as wire.
DC and low frequencies are blocked by capacitors.
This blocking effect is called REACTANCE ( XC ) and it's similar to resistance but it depends on frequency.
XC = 1 / ( 2 π f C )
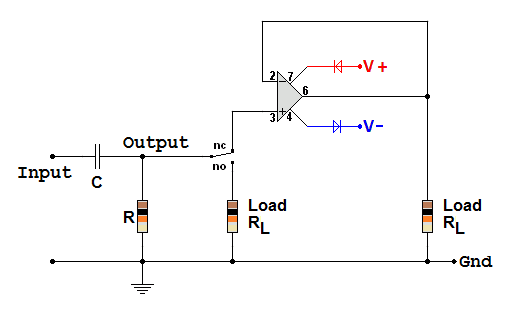
The circuit above shows an RC high pass filter connected to a choice of two loads. SIMULATION
Inductors pass DC and low frequencies just like wire although they often have more resistance than a short wire.
At high frequencies, inductors block AC signals.
This blocking effect is called REACTANCE ( XL ) and it's similar to resistance but it depends on frequency.
Inductors have a couple of disadvantages. They can be bulky and waste heat can be generated due to the DC resistance of the wire making them less efficient.
XL = 2 π f L
Capacitor - The current leads the voltage. To charge or fill a capacitor, a current has to flow. As it fills, the voltage across the capacitor builds up, like the water level in a bucket. Once it's nearly full, this voltage reaches its maximum and the current dies away to zero. Note that this is the voltage across the capacitor and not the external voltage causing it to charge in the first place.
Inductor - The current lags the voltage. Inductors only have a voltage across them if the current is changing. With a steady current, the voltage across an ideal inductor would be zero because its resistance is zero. Whenever the current changes, the altering magnetic field induces a back EMF that opposes the change in current.
Phase - This is the angle 90o or, in radians, π / 2 between the voltage and the current. This is a quarter of a cycle of the wave.
Subject Name Level Topic Name Question Heading First Name Last Name Class ID User ID
|
Q: qNum of last_q Q ID: Question ID Score: num correct/num attempts Date Done
|
Question Text
image url
Help Link
Add Delete Clone Edit Hardness
Contact, Copyright, Cookies and Legalities: C Neil Bauers - reviseOmatic V4 - © 2016 to 2026
Hosted at Akamai Cloud - London
Please report website problems to Neil