
RANDOM PAGE
SITE SEARCH
LOG
IN
SIGN UP
HELP
To gain access to revision questions, please sign up and log in.
A2
aDefinitions
- Modulation is the process of encoding information onto a carrier wave.
- Digital modulation samples the information at regular time intervals.
- Each measurement of the analogue signal is called a sample.
bSampling Rate
The sampling frequency must be at least double the highest frequency being sampled. (Nyquist).
cResolution
The size (usually in Volts) of the smallest step in the reconstructed analogue signal.
You also need to know how many steps there are. This is a 2n problem. A 5 bit converter has 25 = 32 steps.
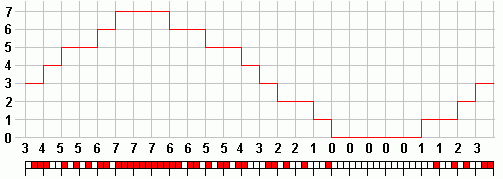
This depends on the number of different values that can be encoded. With 4 a bit sample any number between 0 and 15 can be stored. If voltages between 0 and 3.2V are to be encoded into 16 levels, each level is 0.2 Volts. This is the resolution measured in Volts. By adding one more bit to each sample, the resolution is doubled to 0.1 volts. Above the image shows a reconstructed three bit signal and the steps are obvious. The lack of quality in the reconstruction is quite serious. Eight bit systems are much better. Sixteen bit systems are used for CD audio and these are superb.
dBit Rate
- This is the number of bits that have to be transmitted per second.
- If you need to sample speech, for tolerable quality the highest frequency is 3000Hz or 4000Hz for better mobile phone quality.
- The sampling rate would need to be double this at 6000 or 8000Hz.
- Eight bit samples give quite good quality so you would need 8 times 6000 or 8000.
- 48000 bits per second would be the minimum acceptable rate and 64000 bits per second would be preferred.
- Using data compression techniques, fewer bits per second are needed.
eAnalogue Modulation
The carrier wave is transmitted even when there is no music, speech or data. It sounds like silence or silence with background noise (hiss and other interference) on a weaker transmission.
- AM - Amplitude Modulation - The amplitude of the carrier is altered.
- FM - Frequency Modulation - The frequency of the carrier is altered. The amplitude remains constant.
- PM - Phase Modulation - Similar to FM, but the phase of the carrier is altered. The amplitude remains constant.
fDigital Modulation
Digital data is transmitted across radio links, over cables and through fibre optics. AM and FM are not ideal for digital systems so other modulation methods are used.
- PAM - Pulse Amplitude Modulation - The amplitude of the pulses is altered.
- PWM - Pulse width Modulation - Pulses are transmitted and their width is altered to encode the information.
- PPM - Pulse Position Modulation - Pulses are transmitted and the timing of the pulses is altered to encode information.
- PCM - Pulse Code Modulation - Pulses that represent binary numbers are transmitted. The binary numbers are decoded to extract the information.
- QAM - Look up Quadrature Amplitude Modulation on Google to see just how complex and advanced a topic digital modulation is. It won't be in the AQA exam!
gPulse Modulation Methods
hPulse Amplitude Modulation
- A stream of pulses is needed.
- The amplitude (height) of the pulses is proportional to the amplitude of the the signal (music, voice, data etc) to be transmitted.
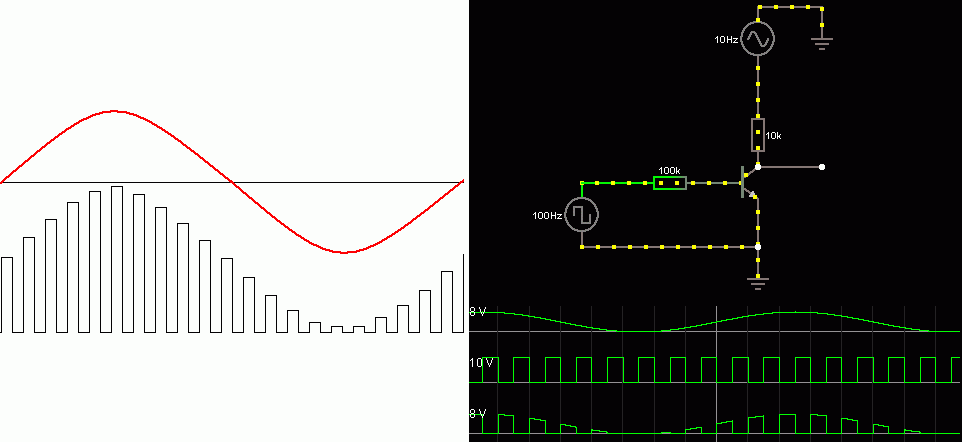
For the Falstad Circuit Simulation, CTRL+Click Pulse Amplitude Modulation
In options, check European Resistors and uncheck Conventional Current.
Note how simple this circuit is. It uses a single transistor.
Alternatively view PAM.txt.
Save or copy the text on the web page. Import the saved or copied text into the Falstad simulator.
Here is the new HTML5 Simulator Site.
iPulse Width Modulation
- A stream of pulses is needed.
- The width of the pulses is proportional to the displacement (height) of the wave.
- Here is a video where you can LISTEN to a pulse switched circuit.
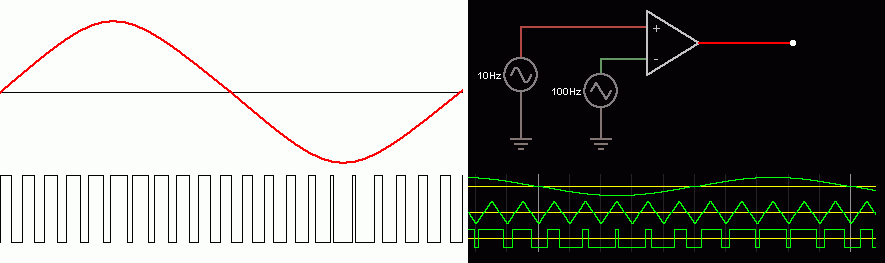
For the Falstad Circuit Simulation, CTRL+Click Pulse Width Modulation
In options, check European Resistors and uncheck Conventional Current.
It uses a single comparator.
Alternatively view PWM.txt.
Save or copy the text on the web page. Import the saved or copied text into the Falstad simulator.
Here is the new HTML5 Simulator Site.
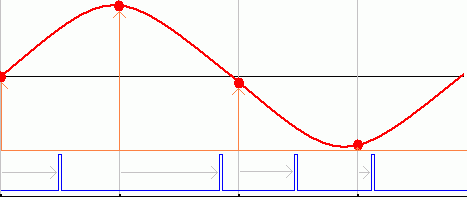
jPulse Position Modulation
- A stream of pulses is needed.
- The fixed width pulses are delayed (relative to a regular clock pulse) by an amount that is proportional to the level of the signal (in red) to be modulated.
- The light grey arrows show the size of the delay.
- The red blobs show the moment when the signal is sampled (measured).
- The vertical gray/orange lines are the regularly spaced sample time intervals.
- The blue pulses are delayed relative to these regularly spaced intervals.
- The delay is proportional to the level of the signal being transmitted.
- The sample level is shown by the orange arrows.
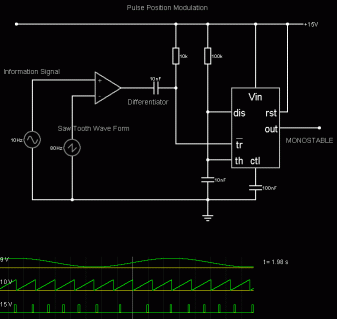
For the Falstad Circuit Simulation, CTRL+Click Pulse Position Modulation
In options, check European Resistors and uncheck Conventional Current.
This circuit uses a comparator, a timing circuit and a monostable.
Alternatively view PPM.txt.
Save or copy the text on the web page. Import the saved or copied text into the Falstad simulator.
Here is the new HTML5 Simulator Site.
kPulse Code Modulation
Encoding and Transmitting
- To encode a transmission, the music or voice is converted into a stream of binary numbers.
- This is Analogue to Digital Conversion.
- This stream of binary numbers is transmitted.
- From this, the original wave can be re-created (always with +/- one bit error).
- This example shows 3 bit encoding. Each sample is converted into a three bit number.
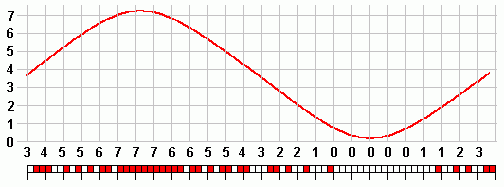
Receiving and Decoding
- In these diagrams above, (red = 1) and (white = 0)
- To decode PCM, the binary numbers are converted back to an analogue signal.
- With the three bit system shown here the reconstruction is not very good at all.
- 8 bit (approx 0.5% error) and 16 bit (minimal error) systems are much better.
- With extra bits, the 'steps' in the staircase get smaller so the reconstruction is better.

lLittle and Big-Endian
Wars have started over less controversial topics.
In the PCM diagrams, 3 was converted into 011.
The war is about whether the most or least significant bit should be transmitted first using a serial link.
Endianness on Wikipedia
reviseOmatic V3
Contacts, ©, Cookies, Data Protection and Disclaimers
Hosted at linode.com, London








