
RANDOM PAGE
SITE SEARCH
LOG
IN
SIGN UP
HELP
To gain access to revision questions, please sign up and log in.
A2
aCable
- Feeder Cable: is used to connect the antenna to the transmitter or receiver.
Advantages
- Ideal for point to point communications as long as a cable is available.
- More secure than radio because not anyone can tune in.
Disadvantages
- Wires can be tapped.
- Computer networks can be "sniffed" (unauthorised listening to data packets).
- Can't be used for mobile devices.
bWire
Normal wire is fine for DC circuits. As soon as the frequency goes above a few hundred hertz, normal wire begins to act like an antenna and signals leak out of or into the cable. This is already a problem with audio frequencies. This leakage is called cross-talk. The solution is to use co-axial cable.
cCoaxial Cable
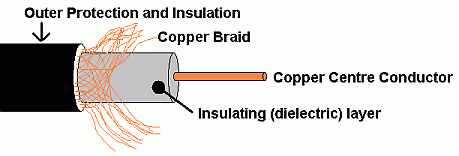
- The outer woven copper braid acts as a screen and the signal is carried on the inner conductor.
- This greatly reduces leakage out of or into the cable.
- These cables work at frequencies up to about 1 GHz.
- As the frequency increases, the signals suffer from more and more attenuation (energy lost as heat or leakage from the cable).
- Once the wavelength is less than about 5 cm, it is more efficient to use wave-guide (pipes) as shown below.

dOpen Wire Transmission Line
- At frequencies below about 30 MHz, open wire feeder is used to connect transmitters to antennas.
- The energy losses are lower than co-axial cable.
- The cable is cheaper than co-axial.

Here is some open wire co-axial cable capable of handling megawatt transmitter powers.

eTwisted Pair

- Twisted Pair cable is used for computer networks and also for telephone wiring.
- The upped frequency limit for CAT-5e cable is about 250 MHz. Using all four pairs, gigabit speeds are possible.
- The twists are carefully designed to cancel out the ability of the cable to act as an antenna.
- This means that signals are contained within the cable.
- Cross-talk (unwanted signal leakage) between the pairs of cables is minimised.
- The cable has good immunity from picking up radio transmissions.
- There is a more expensive shielded version of this cable that is even better at keeping out interfering signals.
fOptical Fibre
Instead of sending radio signals down cables, light flashes can be sent down optical fibres.
 Attribution
Attribution
Advantages
- Better security - very hard to tap a fibre without being noticed.
- Longer cable runs
- Greater bandwidth.
- Not affected by electromagnetic interference.
- Can connect between buildings with different earth potentials. These would could cause problems with a copper wired system.
- Not effected by near-miss lightning strikes
- Lower cost for 2 to 3 km fibre runs. CAT5 twisted-pair is limited to 100 metres.
- Less likely to be stolen as there is no copper which has a high scrap value.
- Carrier signals on different frequencies (colours) can be used to increase the capacity (frequency division multiplexing).
- Single mode or monomode fibre has a very thin inner glass layer.
- This is so thin that it behaves like a wave guide and the light can't follow different paths.
- This reduces the dispersion and makes longer fibres possible. 30km.
Disadvantages
- Attenuation is still a problem and this limits the maximum cable length
- Dispersion is still a problem and this also limits the maximum cable length
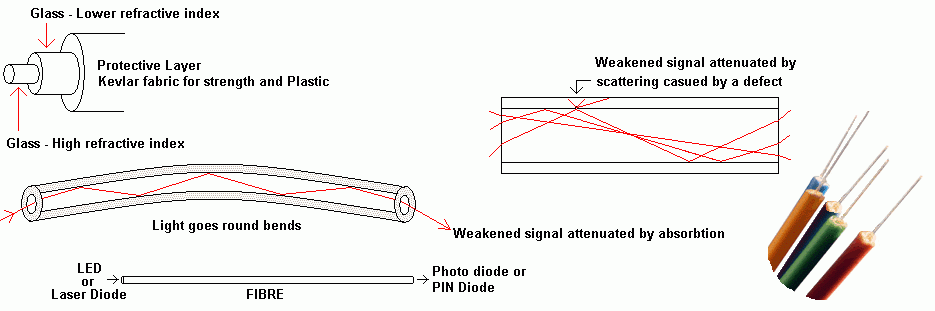
- Scattering occurs when there are imperfections in the fibre. This causes attenuation or energy loss.
- Higher installation cost for small networks. For major backbones fibre works out cheaper per megabit of bandwidth.
- Optical fibres can be fragile although they are reinforced with kevlar fibres and an outer protective plastic layer
- Optical fibres are difficult to connect to the transmitting light source and the receiving light detector. A complex cutting and polishing operation is needed to make the fibre ends flat and free from dirt or imperfections.
gTotal Internal Reflection
Fibre optics rely on a physics phenomenon called Total Internal Reflection. The same effect makes gems sparkle. Surfaces under water that trap air look silvery. Lake mirages in the desert are yet another example. In the diagram above, the light beam is trapped in the inner core of glass. Like this, light can travel long distances and go round corners too.
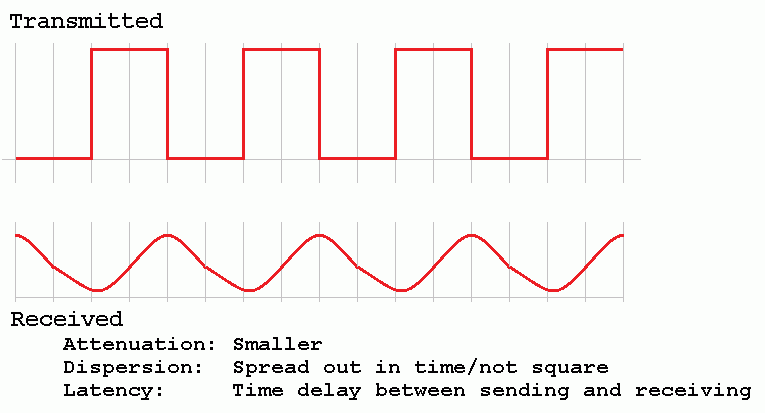
hAttenuation
- Attenuation is the weakening of the signal with distance from the transmitter.
- Energy is lost because of scattering due to imperfections in the glass and between the glass layers.
- Energy is lost because a proportion of the light is absorbed by the glass in the fibre.
- Using special, very clear glass helps.
- Infra-red is used because this suffers less from absorption.
iLatency
This is how long it takes for a signal to travel from the sender to the receiver. On TV interviews, the latency or delay becomes noticeable if satellite or slow internet links are being used.
jDispersion
- Dispersion is the spreading out in time of the transmitted pulse.
- If the pulses spread too much, they merge into each other and the receiver can no longer detect them.
- The light is dispersed because not all the light follows the same path.
- Light that zigzags more, takes longer to arrive.
- This effect is minimised by making the inner glass layer very thin. Look up single mode fibre.
- The light is dispersed for a second reason.
- Different radio or light wavelengths travel at slightly different speeds so the pulses of radio or light spread out as they go down the fibre.
- Square radio pulses contain multiple frequencies which travel at different speeds causing the pulse to spread out.
- Using monochromatic ( single frequency LASER ) light helps.
- Modulating the light beam creates sidebands on different frequencies so the problem is not completely solved.
kRadiation
- Leakage of energy out of the fibre.
- Sharp bends cause light to hit below the critical angle so total internal reflection no longer occurs.
- Less than perfect connections in the fibre could leak energy.
lWireless - Mobile Communication
mFree Space
Radio Waves / Electromagnetic Radiation will travel through free space (Air or a vacuum).
Advantages
- One transmitter can send to many receivers.
- Ideal for mobile use. Both the sender and the receiver can be mobile.
- Signals can be encrypted to prevent unauthorised decoding.
Disadvantages
- Potentially insecure because anyone can tune into a radio transmission.
- Reception can be damaged by freak weather or unusual sun spot activity.
- Reception can be damaged by other transmissions on the same or close frequencies.
- Thunder storms generate radio noise spikes that interfere with reception.
- Some types of industrial, medical and radar systems generate strong signals that can interfere with radio communications.
- Some domestic appliances like power-line network adapters create serious interference across wide parts of the spectrum.
nAir
Ultrasound transducers are used to send and detect signals sent through air.
- Car reversing collision warning.
- Burglar alarm movement sensing.
- Distance measurement by timing how long an ultrasonic pulse takes to echo back.
Normal sound is used too but suffers more from interference due to natural background noise.
reviseOmatic V3
Contacts, ©, Cookies, Data Protection and Disclaimers
Hosted at linode.com, London








