
RANDOM PAGE
SITE SEARCH
LOG
IN
SIGN UP
HELP
To gain access to revision questions, please sign up and log in.
A2
Terminology
- Supersonic. The frequency is too high for human hearing.
- Heterodyne. The sum and difference beat frequencies produced when two signals on different frequencies are mixed.
- Sensitivity: The ability to receive weak signals.
- Selectivity: The ability to tune in one station and reject others on nearby frequencies.
- RF: Radio frequency.
- IF: Intermediate frequency.
- AF: Audio frequency.
- AGC: Automatic Gain Control.
The Supersonic Heterodyne Receiver
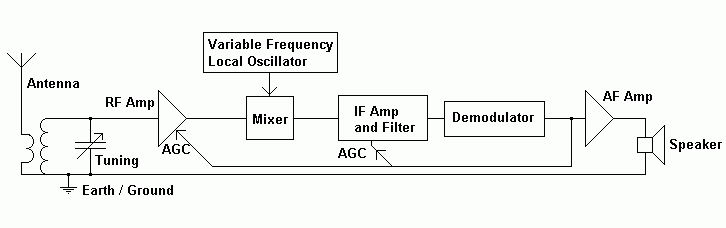
The superhet receiver works much better than the simple receiver for the following reasons ...
- The intermediate frequency filter provides good selectivity.
- It is on a fixed frequency so there is no need to use expensive tuning capacitors.
- Tuning is achieved with a Local Oscillator and a Mixer.
- The RF and AF amplification provide good sensitivity and a loud output of only one station.
Superhet disadvantages ...
- It is more complex and expensive.
- The mixer responds to an Image Frequency or Second Channel.
- This problem can be minimised with a simple tuned circuit filter between the antenna and receiver.
- At the antenna a band pass filter can be used to reject all frequencies outside the desired band.
- The local oscillator needs to produce a pure sine wave on a single frequency. This is hard to achieve. If the oscillator signal is distorted, there will be harmonics (multiples of the wanted frequency). The mixer can mix these harmonics with unwanted signals from the antenna and the correct IF is produced. These are called spurious responses. Top quality receivers which minimise such problems are costly! Distortion in the mixer causes similar problems.
Superhet Subsystems
Antenna
The antenna will often be a half wave dipole. This is ideal for short wave radio between 1.6MHz and 30 MHz. At lower frequencies a ferrite rod antenna is often used.
Tuning
A simple LC tuned circuit selects the desired radio frequency. The image frequency is generally so different from the wanted frequency that this single stage of tuning is sufficient.
Radio Frequency (RF) Amplifier
This amplifies the radio frequency. If the RF amplifier has a variable gain design, automatic gain control can be applied here.
Local Oscillator
In cheap AM radios, this oscillator is 455kHz higher in frequency than the wanted signal. It could be 455kHz lower but this might cause more unwanted image signal problems.
In FM radios, the local oscillator is 10.7 MHz above the wanted signal.
Mixer
- When two frequencies are mixed, heterodyne signals are produced.
- The original two frequencies are still present in the output.
- The sum of the two input frequencies is present.
- The difference between the two input frequencies is present.
- if the input frequencies are F1 and F2 the output frequencies will be ...
- F1
- F2
- F1 + F2
- F1 - F2
- Only one of the sum or difference signals is useful. The other one, called the image frequency, is filtered out.
Mixer Example
- To receive a 1MHz broadcast, the local oscillator is set to 1.455MHz.
- The wanted heterodyne signal will be on 455kHz.
- The IF amplifier is tuned to this frequency.
- The image frequency is 1.910 MHz because (1.910 - 1.455) also is equal to 455 kHz.
- This unwanted image is filtered out. A single tuned circuit at the antenna is usually sufficient.
Intermediate Frequency Amplifier
- The IF Amplifier amplifies the wanted heterodyne signal on 455kHz.
- The IF amplifier will often include automatic gain control.
Intermediate Frequency (IF) Filtering
- The IF amplifier stage includes several high quality fixed tuned circuits.
- It is also possible to use ceramic filters. These work even better than tuned circuits.
- Quartz crystals can be used for excellent filtering.
- This filtering provides excellent selectivity.
- The wanted station can be heard even if the signal is weak and there are stronger stations on nearby channels.
Demodulator
Sometimes called the Detector.
The audio (or digital data) is separated from the modulated carrier.
Automatic Gain Control
- It is designed to keep the output from the receiver constant even if the received signal is repeatedly fading and getting stronger.
- The IF amplifier or Demodulator output is measured.
- If the output is too large, the receiver gain is decreased.
- If the output is too small, the receiver gain is increased.
- This is a closed loop control system with negative feedback.
AF Amplifier
- This amplifies the audio signal from the demodulator to a level suitable to drive a loudspeaker.
- Often a one chip circuit is used here such as the LM386 chip.
Superhet Signals
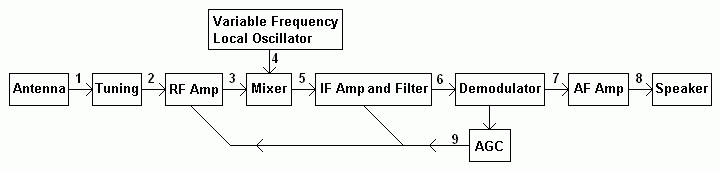
- A wide range of radio frequency signals including the unwanted image signal or second channel.
- A much smaller range of radio frequency signals.
The unwanted image frequency is removed by the tuned circuit. This works well but might not be 100% removed.
Other frequencies close to the wanted frequency are NOT removed.
- An amplified copy of the smaller range of radio frequency signals.
- A pure sine wave signal generated by the local oscillator. To tune in different stations, this frequency has to be altered.
- The sum and difference frequencies produced by mixing 3 with 4.
The wanted input frequencies is mixed to become the intermediate frequency.
The other input frequencies are mixed and fall above or below the intermediate frequency.
- The wanted intermediate frequency at a higher signal level. All the other unwanted signals have now been filtered out.
- A small audio signal.
- A much larger audio signal sufficient to drive the speaker.
- A DC voltage proportional to the radio frequency signal strength.
The DC voltage is fed back and used to reduce the gain of the RF amplifier and IF amplifier.
It the antenna signal is very strong, the receiver gain is reduced.
If the antenna signal is weaker, the
receiver gain is increased
This is a closed loop control system. It uses negative feedback.
It measures the IF output signal strength and alters the receiver gain to keep this signal strength constant.
The audio level does not increase or decrease if the RF signal gets stronger or weaker.
Satellite TV LNB
Satellite TV is transmitted at a frequency that is so high that low cost co-axial cables can't be used to connect the dish to the receiver. The solution is to use superhet technology. The LNB (low noise block) mounted at the focal point of the dish antenna, uses a local oscillator and mixer to down-convert the satellite frequencies to a much lower frequency. These frequencies can be handled with low cost cables and a relatively simple satellite receiver design.
Audible Heterodynes
To receive Morse code and digital-text with amplitude, frequency or phase modulated signals, the radio frequency is mixed with another locally generated signal to produce an audible heterodyne at about 600 Hz. Without this the Morse would sound like a faint hiss being keyed on and off.
A common and unpleasant cause of interference is unwanted heterodyne signals. These sound like a continuous whistle or whine in the background of the wanted signal. They are caused by carrier waves on a frequency very similar to the wanted frequency. Top quality radio receivers include notch filters to remove the unwanted heterodyne signal.
Circuits
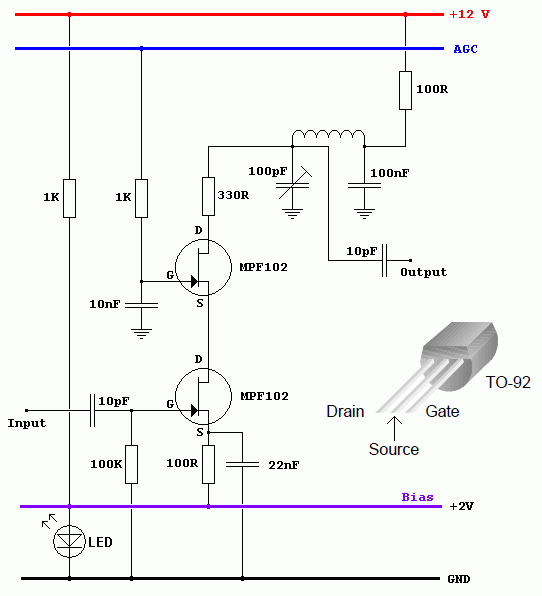
IF Amplifier - Not in the AQA Exam
A Possible IF Amplifier circuit with AGC.
reviseOmatic V3
Contacts, ©, Cookies, Data Protection and Disclaimers
Hosted at linode.com, London




