 Home
Home
rOm
Quest
Glossary
Random
Page
Search
Site
Lush
Sim
Class
Subject
Images
Help
FAQ
Sign
Up
Log
In
WANTED: Individual or team to take over this project. I'm in my 70's and want to put my feet up. Contact details in footer.
Operational amplifiers have a very high open loop gain, a high input impedance and a low output impedance.
Amplifiers increase the magnitude of the input signal.
With this amplifier, the output voltage is bigger and it's inverted.
Amplifiers have one or more of the following properties.
-
The output voltage may be bigger than the input voltage
-
The output current may be bigger than the input current
-
The output power may be bigger than the input power
-
High input impedance (AC equivalent of resistance)
-
Low output impedance (AC equivalent of resistance)
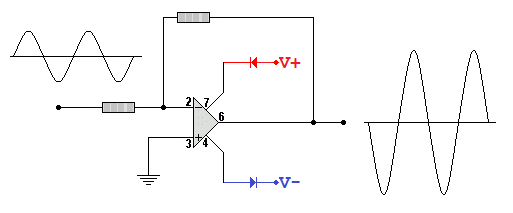
The 741 Operational Amplifier
Data Sheet
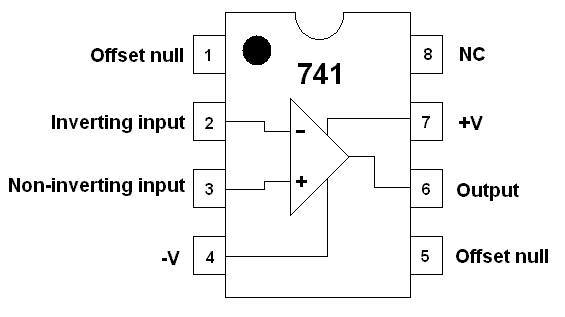
Pins
-
Offset Null - Rarely used. It can be used to to adjust for small errors in the two inputs so zero volts in gives zero volts out.
-
Inverting Input - If this voltage goes up, the output voltage will go DOWN unless the Op Amp is already saturated.
-
Non-Inverting Input - If this voltage goes up, the output voltage will go UP unless the Op Amp is already saturated.
-
The minus supply - Sometimes this is connected to zero volts ( ground ).
Sometimes it's connected to a voltage between -5V and -18V or more for a few specialised op amps.
-
Offset Null - Rarely used. It can be used to to adjust for small errors in the two inputs so zero volts in gives zero volts out.
-
The Output - In an ideal Op Amp, the maximum and minimum output voltage is equal to the power supply voltages.
In a real life Op Amp, these voltages are 2 to 3 Volts less.
-
The plus supply - Voltages from +5V to +18V are common.
There are specialist and more expensive Op Amps with a higher voltage ratings.
-
No Connection - This pin is not used.
The 741 is a low cost operational amplifier. It has ...
-
A very high open loop gain (close to infinity)
-
Very high input resistance (close to infinity)
-
Low output resistance (close to zero)
-
A rather poor gain bandwidth product compared with slightly more expensive op' amp's.
-
It's very easy to use. Higher performance devices often suffer from unwanted parasitic oscillation and are much harder to work with. A technique called equalisation prevents this.
It can be used to make ...
-
EVERYONE
-
Comparators (compare two voltages)
-
Inverting Amplifiers (make the input signal bigger and invert it)
-
Non Inverting Amplifiers (make the input signal bigger without inverting it)
-
Summing Amplifiers (add two or more input voltages and amplify and invert the result)
-
AS Level
-
Voltage Follower. A non-inverting amplifier with a high power or current gain and a voltage gain of one.
-
Schmitt Trigger (compare the input with two different reference voltages).
-
A Level
-
Difference (subtracting) Amplifiers (subtract two input voltages and amplify the result)
Feedback Resistors >= 1k and <= 1M
-
These are usually in the range 1k to 1M.
-
Resistors less than 1k might lead to currents greater than a typical op-amp can supply.
-
Resistors greater than 1M might allow op-apm leakage currents to become important and the circuit will not beave as expected.
-
There are specialised op-apms for instrumentation or power systems where these limits don't apply.
Operational Amplifier Ideal and Typical Properties
|
Characteristics |
Ideal |
Real - Depends on the model |
|
GAIN: Open Loop |
Infinity |
> 100000 or 1000000 typical |
|
Input Resistance: (Impedance) |
Infinity |
> 1M (Bipolar) > 1000M (FET) |
|
Output Resistance: (Impedance) |
Zero |
100 - 1000R |
SATURATION High:
Highest Output Voltage |
Positive Power Supply Voltage
Typical value = 12 V.
|
Two volts below the positive supply
Typical value = 10 V.
|
SATURATION Low:
Lowest Output Voltage |
Negative Power Supply Voltage
Typical value = -12 V.
|
Two volts above the negative supply
Typical value = -10 V.
|
|
Gain Bandwidth Product: |
Infinity |
1 - 20MHz |
|
Input offset voltage: |
Zero |
Often Adjustable to Zero
|
Subject Name
Level
Topic Name
Question Heading
First Name
Last Name Class ID
User ID
Question Text
image url
Help Link
Add
Delete
Clone
Edit
Hardness
Help Text
Debug
- You can attempt a question as many times as you like.
- If you are logged in, your first attempt, each day, is logged.
- To improve your scores, come back on future days, log in and re-do the questions that caused you problems.
- If you are logged in, your most recent wrong answers get remembered. This might help you and your teacher to correct your understanding.
- In the grade book, you can delete your answers for a topic before re-doing the questions. Avoid deleting unless you intend re-doing the questions very soon.


