 Home
Home
rOm
Quest
Glossary
Random
Page
Search
Site
Lush
Sim
Class
Subject
Images
Help
FAQ
Sign
Up
Log
In
Definitions
-
Modulation is the process of encoding information onto a carrier wave.
-
Digital modulation samples the information at regular time intervals.
-
Each measurement of the analogue signal is called a sample.
Sampling Rate
The sampling frequency must be at least double the highest frequency being sampled. (Nyquist).
Resolution
The size (usually in Volts) of the smallest step in the reconstructed analogue signal.
You also need to know how many steps there are. This is a 2n problem. A 5 bit converter has 25 = 32 steps.
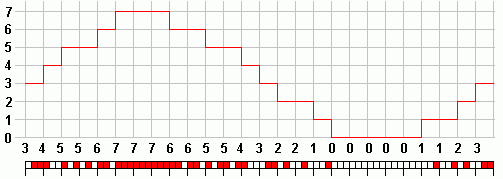
Resolution depends on the number of different values that can be encoded. With 4 a bit sample any number between 0 and 15 can be stored. If voltages between 0 and 3.2V are to be encoded into 16 levels, each level is 0.2 Volts. This is the resolution measured in Volts. By adding one more bit to each sample, the resolution is doubled to 0.1 volts. Above the image shows a reconstructed three bit signal and the steps are obvious. The lack of quality in the reconstruction is quite serious. Eight bit systems are much better. Sixteen bit systems are used for CD audio and these are superb.
Bit Rate
-
This is the number of bits that have to be transmitted per second.
-
If you need to sample speech, for tolerable quality the highest frequency is 3000Hz or 4000Hz for better mobile phone quality.
-
The sampling rate would need to be double this at 6000 or 8000Hz.
-
Eight bit samples give quite good quality so you would need 8 times 6000 or 8000.
-
48000 bits per second would be the minimum acceptable rate and 64000 bits per second would be preferred.
-
Using data compression techniques, fewer bits per second are needed.
Analogue Modulation
The carrier wave is transmitted even when there is no music, speech or data. It sounds like silence or silence with background noise (hiss and other interference) on a weaker transmission.
-
AM - Amplitude Modulation - The amplitude of the carrier is altered.
-
FM - Frequency Modulation - The frequency of the carrier is altered. The amplitude remains constant.
-
PM - Phase Modulation - Similar to FM, but the phase of the carrier is altered. The amplitude remains constant.
Digital Modulation
Digital data is transmitted across radio links, over cables and through fibre optics. AM and FM are not ideal for digital systems so other modulation methods are used.
-
PAM - Pulse Amplitude Modulation - The amplitude of the pulses is altered.
-
PWM - Pulse width Modulation - Pulses are transmitted and their width is altered to encode the information.
-
PPM - Pulse Position Modulation - Pulses are transmitted and the timing of the pulses is altered to encode information.
-
PCM - Pulse Code Modulation - Pulses that represent binary numbers are transmitted. The binary numbers are decoded to extract the information.
-
QAM - Look up Quadrature Amplitude Modulation on Google to see just how complex and advanced a topic digital modulation is. It won't be in the A Level exam!
Subject Name
Level
Topic Name
Question Heading
First Name
Last Name Class ID
User ID
Question Text
image url
Help Link
Add
Delete
Clone
Edit
Hardness
Help Text
Debug
- You can attempt a question as many times as you like.
- If you are logged in, your first attempt, each day, is logged.
- To improve your scores, come back on future days, log in and re-do the questions that caused you problems.
- If you are logged in, your most recent wrong answers get remembered. This might help you and your teacher to correct your understanding.
- In the grade book, you can delete your answers for a topic before re-doing the questions. Avoid deleting unless you intend re-doing the questions very soon.

