
RANDOM PAGE
SITE SEARCH
LOG
IN
SIGN UP
HELP
To gain access to revision questions, please sign up and log in.
Everyone
Pulsed switching circuits can be quite noisy. Click the links for examples ...
If full power were applied to the motors when they were not spinning, the current would be so great that the power grid would fail. There might also be some wheel spin - on a train! and damage to the motors. Once the motors are running, there is Back EMF which reduces the current to a safer level. This is why the power has to be increased gradually.
This speed controller works in the same way.
- It uses a variable frequency 555 astable.
- The astable triggers a monostable that produces pulses of a fixed width.
- At lower frequencies, the monostable pulses are infrequent and the output is high about 20% of the time.
- As the frequency increases, the fixed width monostable pulses get closer together increasing the "Duty Cycle" or the "Mark Space Ratio". This increases the power to the motor. The frequency can be increased until the monostable is triggered with a high output more than 90% of the time.
- The monostable output drives the MOSFET which in turn drives the motor.
- The 1N4001 diode prevents back EMF pulses by allowing the motor current to die away gradually when the MOSFET turns off. This protects the MOSFET.
- When Ra is adjusted, if its resistance becomes too small, the 555 astable stops oscillating.
- The cure for this is the 1K fixed resistor in series with the 100k pot.
- If the astable frequency becomes too high, the monostable will be triggered while its output is already high, These trigger pulses will be ignored and the power output will be lower than expected. Careful component choices would prevent this situation.
- This circuit can drive computer heat sink fans or bigger motors if the MOSFET is bolted to its own heat sink. Scaled up versions of this circuit control the speed of electric trains. On an electric train, you might hear the variable frequency whine coming from the control circuits.
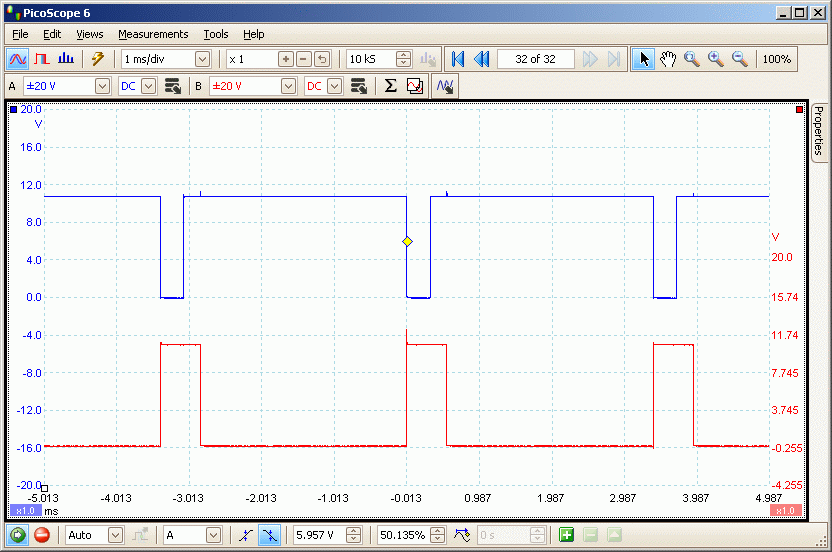
This screen shot shows the astable (Blue) producing fixed width monostable pulses (Red) with about 20% duty cycle.
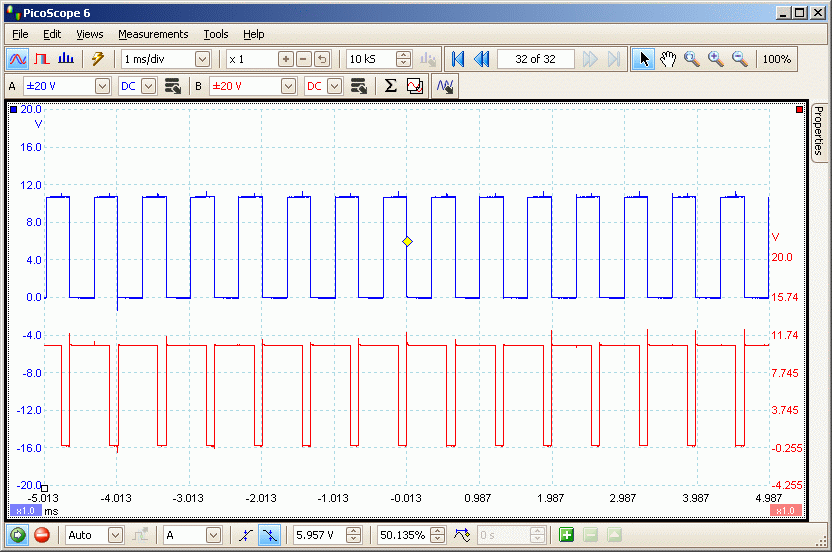
This screen shot shows the astable (Blue) producing fixed width monostable pulses (Red) with about 90% duty cycle.
Yet Another Speed Controller
A thermistor in a voltage divider generates a temperature dependent voltage. This is amplified and used to control the 555 timer. The frequency and mark space ratio (duty cycle) vary depending on the control voltage. This makes a cooling fan run fast if it's hot or slowly if it's cool. The potentiometer is used to adjust the threshold temperature where the circuit starts to operate. This is a 12 Volt circuit (depending on the motor).
reviseOmatic V3
Contacts, ©, Cookies, Data Protection and Disclaimers
Hosted at linode.com, London





