
RANDOM PAGE
SITE SEARCH
LOG
IN
SIGN UP
HELP
To gain access to revision questions, please sign up and log in.
Everyone
aResistance is Measured in Ohms
In a simple circuit, the resistor limits the current to a
small steady safe level.
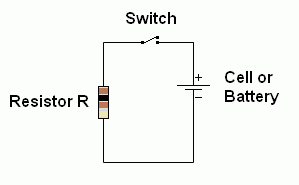
|
Without a current limiting resistor, the current is very
large and possibly dangerous. There is a fire risk.
This is called a short circuit.
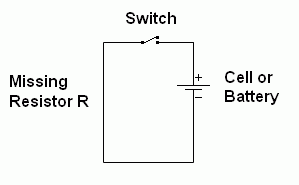
|
bWhat Resistors Do
- Resistors limit the current flowing to a smaller safe level.
- Two or more resistors can be used as a voltage divider.
- Voltage dividers can use fixed resistors.
- Voltage dividers can use thermistors or LDRs to make temperature or light sensors.
- Voltage dividers can use potentiometers to make angle sensors.
- Voltage dividers can use potentiometers to make volume controls.
- A timing resistor is used in conjunction with a capacitor to make a timing circuit.
- A pull-up resistor increases the voltage, usually close to the positive power supply voltage.
- A pull-down resistor drops the voltage close to zero or perhaps to the negative power supply voltage.
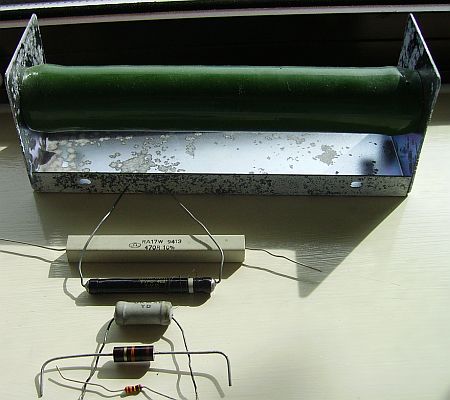
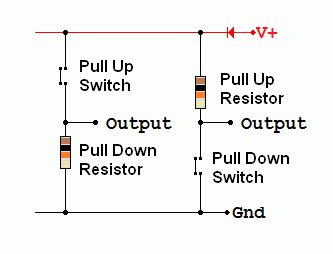

Working from the top down in the image above.
- Wire Wound: Designed to dissipate a lot of heat. Used in very high power situations. 100 Watt resistor.
- Wire Wound: Designed to dissipate heat. Used in high power situations. 10 Watt resistor.
- Wire Wound: Designed to dissipate less heat. Used in lower power situations. 5 Watt resistor.
- Wire Wound: Designed to dissipate less heat. Used in lower power situations. 5 Watt resistor.
- Carbon film: Cheap, not very stable over time, might generate circuit noise. Half Watt resistor.
- Metal Oxide: Slightly more expensive than carbon film, more stable over time, less circuit noise, Quarter Watt Resistor.
cResistor Construction
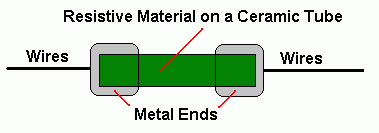
A typical resistor structure is shown above. The whole item is coated in paint/plastic and the colour code stripes added last.
dPower Ratings
Resistors can get hot. They must be able to dissipate (get rid of) this heat. Some commonly available power ratings are 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 1, 2.5, 5, 10, 25 and 50 Watts.
eSymbols
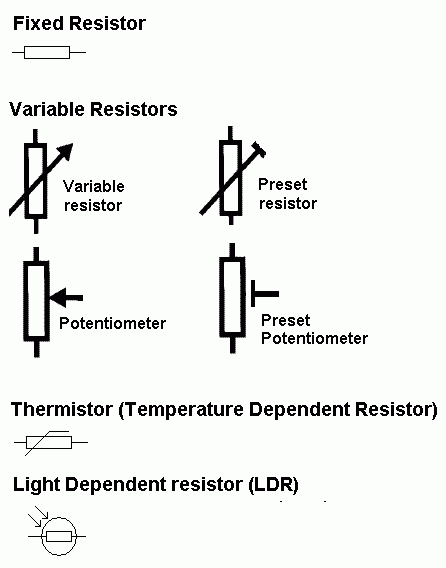
fTypes
| Type |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Carbon Film 
|
|
- Unstable because resistance changes over time
- Resistance changes with temperature
- Can cause noise in circuits. The noise is caused by fluctuations in contact resistances between the carbon granules.
- Not very accurate (poor tolerance)
|
| Metal Oxide 
|
- More accurate
- More stable
- Less noise
|
- More expensive (still remarkably cheap though)
|
| Wire Wound 
|
- Very stable
- Accurate
- Good at dissipating heat
On the left is a damaged resistor where you can see the wire windings.
|
- Most expensive
- Wire winding is inductive so these can't be used in circuits involving radio frequencies.
|
| Wire Wound Aluminium Coated |
- Like normal wire wound but they can be bolted to a heat sink.
|
- Rated at up to 50 Watts.
- Most expensive
- Wire winding is inductive so these can't be used in circuits involving radio frequencies.
|
| Light Dependent Resistors 
|
- Resistance varies with the light level.
- LDRs are used to measure the light level.
- They are used in light meters for photography and for systems that turn on lights when it gets dark.
- The LDR is normally used with a fixed resistor. This prevents too much current flowing when the light is very bright. It also converts the varying light level into a varying voltage.
|
- Must be protected in bright light. The current must be limited to a safe level with a second fixed resistor.
- They are slow to react so they are not used with fibre-optic or other optical communications systems.
|
| Potentiometers 
Here is a flash animation for a potentiometer. |
- Uses include light dimmers, volume controls, tone controls and voltage adjusters.
- They can be pre-set and adjusted with a small screw driver or adjusted with a knob.
- Potentiometer - uses all three pins and works as a voltage divider.
- Variable Resistor - uses only two pins.
|
- Corroded tracks can create nasty noises when the pot is adjusted.
|
| Surface Mounted 
|
- Surface Mounted - 1 or 2 mm across.
- Small (minute)
|
- These can be too small for the average amateur constructor to use!
- Too small to colour code or label. If you mix them up, you are in trouble.
- Capacitors look the same as resistors.
|
gZero Ohm Resistors
Zero ohm resistors exist. These are used instead of wires because robotic circuit board assembly machines are already able to work with standard resistor shapes. A whole new robot would be needed to work with wires so zero ohm resistors were invented.
reviseOmatic V3
Contacts, ©, Cookies, Data Protection and Disclaimers
Hosted at linode.com, London












