WANTED: Individual or team to take over this project. I'm in my 70's and want to put my feet up. Contact details in footer.
| GCSE Basics Atom BCD Binary Conductors Current Energy Equations Insulators Maths Power Resistance Safety SI Units Superconductors Symbols >Transfer Characteristics< Voltage |
Basics Transfer Characteristics |
|
Transfer Characteristics are usually shown as graphs of the input and output voltages or currents of components or circuits.
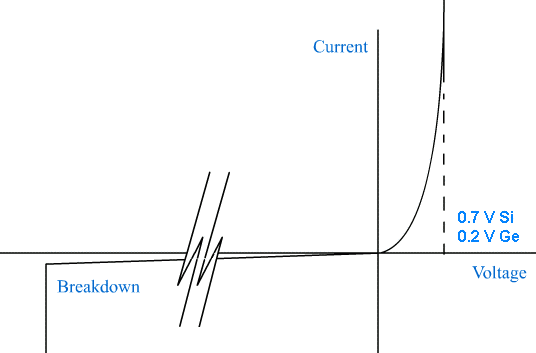
When current is flowing normally, there are about 0.7 volts across a typical silicon diode. When reverse biased, at some voltage the diode breaks down and a large current flows. (often > 50 V)
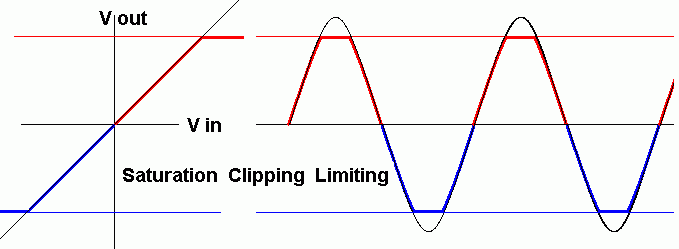
A Transfer Characteristic (left) and a normal Voltage time graph (right). This happens because the circuit can't output a voltage greater than the power supply voltage so the output voltage is limited.
This is a mathematical description of the input output relationships of component or circuit currents or voltages.
For inverting op-amps Vout = - Vin Rf / R1 and Vout < Vsupply
Subject Name Level Topic Name Question Heading First Name Last Name Class ID User ID
|
Q: qNum of last_q Q ID: Question ID Score: num correct/num attempts Date Done
|
Question Text
image url
Help Link
Add Delete Clone Edit Hardness
Contact, Copyright, Cookies and Legalities: C Neil Bauers - reviseOmatic V4 - © 2016 to 2025
Hosted at Akamai Cloud - London
Please report website problems to Neil