WANTED: Individual or team to take over this project. I'm in my 70's and want to put my feet up. Contact details in footer.
| A Level Signal ADC Flash ADC Ramp DAC Summing Distortion Problems Regenerator Sample and Hold >Sampling< Serial and Parallel signal to noise ratio |
Signal Sampling |
|
Resolution is the size of the smallest step measured in whatever units are appropriate.
Using four bit samples, only 24 = 16 levels are available. This means the signal can not be recreated with great accuracy. The Resolution is poor. Increasing the number of bits per sample improves the resolution. If one extra bit is used in each sample, the resolution doubles. Eight bits per sample give 256 levels and the signal can be reconstructed quite well. The error is one part in 256 which is better than 0.5% error. With 16 bit samples, the error is one part in 65536. This is superbly accurate. CD audio uses this resolution.The carrier signal used to carry data or the clock frequency used to sample data needs to be on a frequency at least double the highest data/music/voice frequency.
This is the number of samples per second.
This rate must be at least double the highest frequency in the information signal to prevent unwanted frequencies appearing in the output. This effect is called aliasing.
The Nyquist Frequency also known as the critical frequency is the highest data/music/voice frequency that can be transmitted. This is half the sampling or carrier frequency.
As the transmission frequency increases, the amount of sampled data that can be encoded also increases. For digital transmissions, UHF and Microwave are preferred over the LF, MF and VHF bands. Fibre-optic is even better due to the exceedingly high frequency of light.
The frequency of light is in the region of 1014 Hz. Theoretically data rates of half this figure should be possible if the light emitting and detecting devices and the fibres could ever be made good enough.
A digital audio transmission takes 8000 samples per second. Each sample is encoded into an 8 bit binary number. So 8 x 8000 = 64 000 bits per second must be transmitted.
Gigabit Ethernet works at 109 bits per second. Assuming 100% of this capacity could actually be used, 1 000 000 000 / 64 000 audio channels would be possible = 15 625 channels. In real life the figure is somewhat lower because Ethernet can never reach 100% capacity.
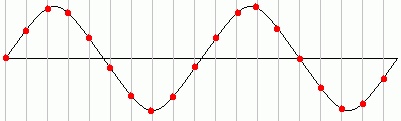
Plenty of Samples - This will work - The original signal can be re-constructed fairly well
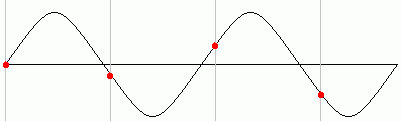
Not Enough Samples - This will not work - The original signal can't be re-constructed
If frequencies above the Nyquist imit or critical frequency are present, there will be unexpected frequencies in the output. These sound unpleasant. A low pass filter fixes the problem and it ensures that no higher frequencies are digitised.
This is also why you are advised to keep pets indoors during firework displays.
|
Poor Sound - Audio Aliasing |
Better Sound - Minimal Audio Aliasing |
If the sampling frequency is too low, unwanted frequencies appear in the re-constructed signal. This problem is known as aliasing. It can often be seen in video recordings where the detail in the recording has a size similar to the pixels in the play-back device. Strange flickering effects can be seen. This is why TV presenters never wear stripy shirts or ties. Other effects include helicopters where the rotor blades appear not to be moving.
Here is a still image with aliasing. The camera resolution is similar to the display resolution. To remove the patterns, the camera resolution needs to be at least double that of the display in both the X and Y directions.

Subject Name Level Topic Name Question Heading First Name Last Name Class ID User ID
|
Q: qNum of last_q Q ID: Question ID Score: num correct/num attempts Date Done
|
Question Text
image url
Help Link
Add Delete Clone Edit Hardness
Contact, Copyright, Cookies and Legalities: C Neil Bauers - reviseOmatic V4 - © 2016 to 2026
Hosted at Akamai Cloud - London
Please report website problems to Neil