WANTED: Individual or team to take over this project. I'm in my 70's and want to put my feet up. Contact details in footer.
| A Level Signal ADC Flash ADC Ramp DAC Summing >Distortion< Problems Regenerator Sample and Hold Sampling Serial and Parallel signal to noise ratio |
Signal Distortion |
|
In an ideal world, electronic circuits would process signals perfectly.
In real life, circuits introduce errors in the output called DISTORTION.
Well designed circuits minimise distortion.
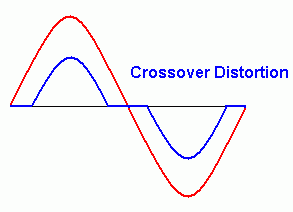
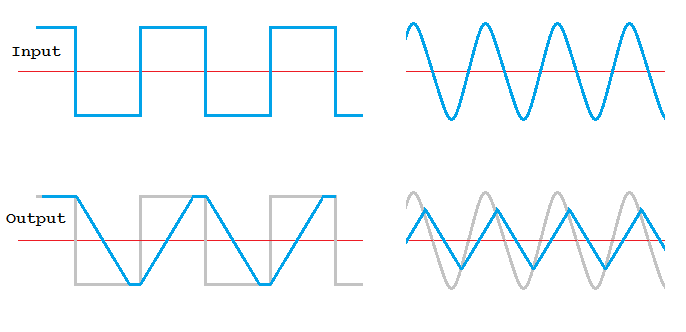
Cross over distortion happens when the input signal is so small that neither device in a push-pull amplifier is turned on. Low input voltages are missing from the output. This can be reduced by BIASING the amplifier MOSFETS and by adding NEGATIVE FEEDBACK to the circuit.
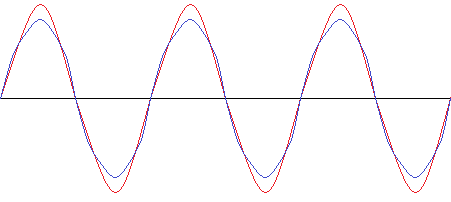
The red wave is what the amplifier should produce. The blue wave is distorted from the wanted shape. There is no clipping. The low input levels are not damaged. NEGATIVE FEEDBACK greatly reduces this type of distortion.
Amplifiers have an upper limit to the rate at which the output can rise or fall. This is called the slew rate.
A sudden input voltage change will cause a less sudden output change. Even sine wave inputs can be damaged. The output tries but fails to keep up with the input changes.
This is somewhat like the 0 to 60 performance figure for a car. If you "floor" the accelerator, it still takes time for the car to build up speed.
Biasing and negative feedback don't help.
The only fix is to use devices with a higher slew rate. Both signals in the diagram below are distorted due to the slow output slew rate.
Distortion occurs when circuits don't reproduce input signals perfectly.
Noise comes from external sources or sometimes from the circuit itself because it's warm. This warmth causes random atom vibrations along with the electrons. This random electron movement, if amplified, appears as a hissing noise in the output.
Subject Name Level Topic Name Question Heading First Name Last Name Class ID User ID
|
Q: qNum of last_q Q ID: Question ID Score: num correct/num attempts Date Done
|
Question Text
image url
Help Link
Add Delete Clone Edit Hardness
Contact, Copyright, Cookies and Legalities: C Neil Bauers - reviseOmatic V4 - © 2016 to 2025
Hosted at Akamai Cloud - London
Please report website problems to Neil