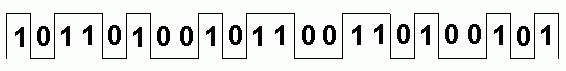RANDOM PAGE
SITE SEARCH
LOG
IN
SIGN UP
HELP
To gain access to revision questions, please sign up and log in.
Everyone
aSignals - Voltages, Currents or Light Pulses which Represent Information
Input transducers produce electrical currents or voltages which are proportional to a measurement of the world.
These are the useful signals. They represent ...
- Music
- Voice
- Temperature
- Light Level
- Pressure
- Water Level
- Time of Day
- Video Images
- Control signals for industrial machines, vehicles and even children's toys.
bNoise - Unwanted and Often Random Voltages or Currents
Noise comes from many sources ...
- Industrial machinery switching on or off
- Thunder storm lightning strikes
( Impulsive Noise )
- Anyone using a radio transmitter
- Fluorescent tubes
- The background hissing noise ...
Radio radiation from the surface of the sun
Any warm or hot electronic component
Carbon film resistors
cAnalogue Signals
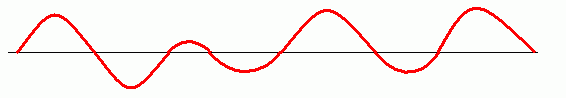
- Analogue signals have an infinite range of values between a minimum and a maximum.
- Analogue signals are processed using Comparators and Amplifiers.
- Analogue signals are usually smoothly varying - there are exceptions like lightning strikes
dDigital Signals
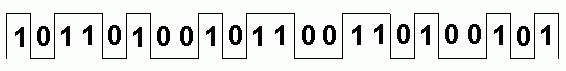
- Digital signals have exactly two values - ON or OFF
- Digital signals are mostly processed using LOGIC CIRCUITS
- Digital signals have the typical square wave shape.
eD to A and A to D Converters
A to D: It's possible to convert analogue signals into digital. The simplest converter is a Comparator. To record voice or music onto a phone, iPod or similar computing device, the analogue signal must be converted into digital.
D to A: It's possible to convert digital signals into analogue. To play music from a phone, iPod or similar device, digital data is first converted into analogue.
reviseOmatic V3
Contacts, ©, Cookies, Data Protection and Disclaimers
Hosted at linode.com, London