
RANDOM PAGE
SITE SEARCH
LOG
IN
SIGN UP
HELP
To gain access to revision questions, please sign up and log in.
Everyone
Solenoids Properties
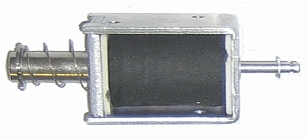
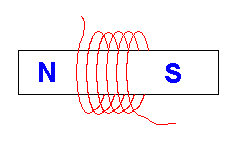
Here is a simple example. Inside the metal frame, there is a coil of copper wire. When a current is passed through the coil, it becomes magnetised and the moveable iron core is pulled into the coil.
- Solenoids are electromagnets.
- They usually have an iron core which greatly increases the magnetic effect of the coil.
- The magnetic effect is used to produce straight line motion.
- Solenoids can be spring loaded so when the current is turned off, the moving part returns to its "off" position.
- Stroke Distance: The size of the movement when the solenoid is turned on.
- Force: For example, the solenoid must produce enough force to operate the valve.
This movement can be used to ...
- operate valves to control liquid flow (hydraulic control systems)
- operate valves to control gas flow (pneumatic control systems)
- lock or unlock doors
- relays are a type of solenoid where the movement is used to operate a switch
- create vibrations, perhaps to ring a bell
- create vibrations because your phone is set to "silent".
Solenoid Driver Circuit
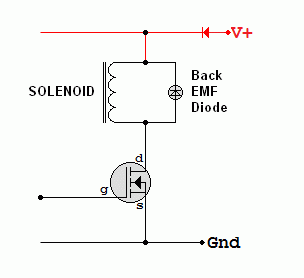
Solenoids are inductive (contain an electromagnet) and they produce a large back EMF if the current flowing is suddenly turned off. To prevent this, put a diode in parallel with the solenoid. This allows the current to die away slowly and the large back EMF is prevented. This also prevents damage to the driver circuit controlling the solenoid.
reviseOmatic V3
Contacts, ©, Cookies, Data Protection and Disclaimers
Hosted at linode.com, London





