
Root Mean Square (RMS) |
|
To gain access to revision questions, please sign up and log in.
In AC circuits, measurements are usually in RMS instead of Peak.
230 Volts RMS Alternating Current (AC) has the same heating effect as 230 Volts Direct Current (DC).
RMS = Root Mean Square
Vrms = 0.7 Vpeak Vpeak = 1.4 Vrms
Alternating voltages (sine waves) have an average voltage of zero because they spend equal times above and below the zero volt line. Clearly it is not useful to say the AC mains supply voltage is zero. The RMS calculation works like this.
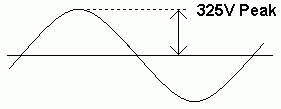
The mains supply in Europe is 230 Volts RMS. The peak voltage is 325 Volts.

0.707 is approximately equal to 0.7 = 1 / sqrt(2)
Prms = 0.5 Ppeak Ppeak = 2 Prms
reviseOmatic V3 Contacts, ©, Cookies, Data Protection and Disclaimers Hosted at linode.com, London